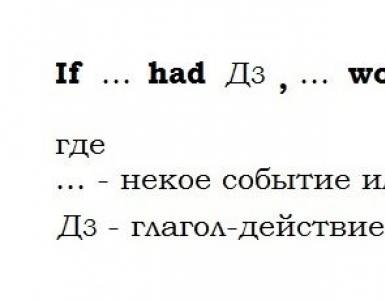Magnetic field inclination. The Earth's magnetic field and its determinants: magnetic inclination
Magnetic inclination, corner I between the geomagnetic field strength vector T and a horizontal plane at the considered point on the earth’s surface (see. Terrestrial magnetism ).n. m is measured from the horizontal plane up or down; N.m. is positive when the vector T directed downward from the horizontal plane, which is the case in the Northern Hemisphere, and negative when T directed upward - in the Southern Hemisphere. Nm varies on the earth's surface from 0° to ± 90°. Curves connecting points on the earth's surface with the same values of N.M. are called isoclines . Isocline I= 0 is called the magnetic equator; point where I= 90°, - the north magnetic pole of the Earth; point where I= - 90°, - south magnetic pole (see. Earth's magnetic poles ). N. m. measured inclinators .
Great Soviet Encyclopedia M.: "Soviet Encyclopedia", 1969-1978
Read also in TSB:
Directional drilling
Directional drilling, a method of drilling a well with a deviation from the vertical along a predetermined curve. N.-n. b. first carried out in the USSR at the Grozny oil fields (1934)...
Charged particle storage devices
Accumulators of charged particles, storage rings, element of accelerators of charged particles with colliding beams. In modern accelerators, the intensity of accelerated particles in one...
Capital accumulation
The accumulation of capital, the transformation of surplus value into capital in the process of capitalist expanded reproduction (see Reproduction). N.K. is at the same time a process in...
Magnetic inclination
Illustration “Magnetic Inclination” from R. Norman’s book “The Newe Attractive” (1581).
Magnetic inclination- the angle by which the arrow deflects under the influence of the Earth's magnetic field in the vertical plane. In the northern hemisphere, the end of the arrow pointing north deviates downwards, in the southern hemisphere - upwards.
Story
Magnetic inclination was discovered by the Chinese scientist Shen Kuo in the 11th century. The first European to describe this phenomenon (in 1544) was the German engineer and astronomer Georg Hartmann. Later, Christopher Columbus discovered that inclination is highly dependent on geographic coordinates. In 1831, the English polar explorer James Ross discovered the magnetic pole in the Canadian archipelago - the region where the magnetic needle occupies a vertical position, that is, the inclination is 90°. In 1909, one of the parties of the Nimrod expedition reached the other magnetic pole of the Earth, located in Antarctica.
see also
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- Magnetic lens
- Magnetic bearing
See what “Magnetic inclination” is in other dictionaries:
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- see Terrestrial magnetism. Samoilov K.I. Marine dictionary. M. L.: State Naval Publishing House of the NKVMF of the USSR, 1941 Magnetic inclination is the angle between the magnetic field strength vector ... Marine Dictionary
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- see Magnetic inclination... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- the angle between the directions of the horizontal line and the magnetic needle, freely rotating on the horizontal axis and located in the plane of the magnetic meridian. M.Sc. at the magnetic poles is 90°, the magnetic needle becomes vertical... ... Technical railway dictionary
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- (deviation), the difference between the direction indicated by the magnetic compass and the true direction of north. This difference is created because the magnetic north pole is not aligned with the true North Pole. As a result, in various areas... ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- the angle formed with the horizontal plane by a magnetic needle rotating around a horizontal axis in the plane of the magnetic meridian. Dictionary of foreign words included in the Russian language. Pavlenkov F., 1907 ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
magnetic inclination- The angle between the horizontal plane and the direction of the full vector of the geomagnetic field. [GOST 24284 80] Topics: gravity and magnetic prospecting... Technical Translator's Guide
magnetic inclination- The angle between the magnetic field strength vector and the horizon plane... Dictionary of Geography
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- the angle between the vector of the Earth’s magnetic field strength (the axis of a freely suspended magnetic needle) and its horizontal component. M.Sc. considered northern if the northern end of the magnetic (see) is inclined downward, and southern if it points upward... Big Polytechnic Encyclopedia
MAGNETIC INCLINATION- the angle between the vector of the Earth's magnetic field strength and the horizontal plane at the considered point on the earth's surface. The direction of the vector is determined by a freely suspended magnetic needle. Magnetic Inclination is considered north,... ... Marine encyclopedic reference book
magnetic inclination- see Magnetic inclination. * * * MAGNETIC INCLINATION MAGNETIC INCLINATION, see Magnetic inclination (see MAGNETIC INCLINATION) ... encyclopedic Dictionary
A compass is a device, the invention of which allowed man to learn to find the location of the planet's poles, thus orienting himself in the area. The blue end of its arrow shows where north is located, and the red end indicates the south direction.
However, when determining cardinal directions using this method, in some cases you can make a mistake. After all, the geographic north and south of the planet do not exactly coincide with the magnetic ones, and it is the location of the latter that is indicated by the compass needle. To be precise in this matter, scientists have introduced a number of concepts, which include magnetic declination and magnetic inclination. They help to detect measurement errors, as well as determine the distance from the poles. In addition, these determinants make it possible to record changes in the field itself that occur over time.
What is the earth's magnetic field?
Our planet can be imagined as a magnet of enormous size. The compass needle is also something like that, only in a miniature version. That is why its ends always point to the magnetic poles of the Earth, taking a position along its magnetic lines.
But what is the source and nature of such a grandiose phenomenon on a planetary scale? People began to be interested in this several centuries ago. At first, versions were put forward that the cause of magnetism was hidden in the earth's core. They thought so until they discovered clear evidence of the influence of solar activity on this natural phenomenon. And then scientists suggested that the source of the earth's magnetism is not in the core.
One of the latest scientific hypotheses, trying to unravel the mystery of what the Earth’s magnetic field is, says the following. Water from the oceans, which occupy a vast territory of the blue planet, evaporates in large quantities under the influence of the energy of the Sun and is electrified, receiving a positive charge. In this case, the earth's surface itself becomes negatively charged. All this provokes the movement of ion flows. This is where the planets themselves appear.
Geographical and magnetic axes
It is not at all difficult to understand what the geographic axis of the Earth is. A planetary ball rotates around it, where certain points remain motionless. In order to understand where the axis is, you need to connect the poles with an imaginary line. But the Earth-magnet or, to put it scientifically, the geomagnetic sphere, also has similar points. If you draw a straight line connecting the north magnetic pole and the south, it will be the magnetic axis of the planet.

Similarly, the Earth magnet has an equator. This is a circle located in a plane that is perpendicular to a straight line called the axis. Magnetic meridians are determined in a manner similar to what has just been stated. These are arcs that bend vertically around the geomagnetic sphere.
Magnetic declination
It is clear that magnetic and geographic meridians, like axes, cannot coincide completely, but only approximately. The angle between them at a certain point on the earth's surface is usually called magnetic declination. It should be noted that for each specific area this indicator, when determined, will be different. And its magnitude helps determine the error between the true direction and compass readings.

Since the direction of the magnetic poles does not coincide with the geographic ones, this error, it turns out, must be taken into account in navigation calculations. This difference can be very important for sailors, pilots and military personnel. On many geographical maps, for convenience, the magnitude of the magnetic declination is indicated in advance.
It is interesting that from the point of view of physics, the true and magnetic poles not only do not coincide, but also seem to be turned upside down, that is, the south corresponds to the magnetic north, and vice versa.
The compass needle is designed to determine the location of the magnetic poles at any point on the Earth. What will happen to the readings of this device directly at the North and South Poles? If the compass is designed in a classical way, then the needle will no longer move freely on the central needle along the body, but will press against it or, on the contrary, deviate. At the northern geographic pole it will pirouette 90° downward, while at the southern pole it will shoot vertically upward with its northern end. The opposite tip of the arrow, that is, the southern one, will behave exactly the opposite.
These metamorphoses do not occur suddenly at one moment when moving towards the poles. It should be noted that the compass needle deviates almost constantly at a certain angle in the vertical direction under the influence of the magnetic field: in the northern hemisphere - downwards, and in the southern hemisphere, respectively, upwards with its northern end. This angle is called magnetic inclination.

A similar phenomenon has been known for a long time and was discovered by the Chinese back in the 11th century. But in Europe it was described much later, in the 16th century. And this was done by an astronomer and engineer from Germany Georg Hartmann.
Measurement methods
The fact that the magnetic inclination changes in a certain way depending on the geographical location and the coordinates that describe it was proven by Christopher Columbus. As you approach the equator, the angle decreases. It becomes equal to zero at the equatorial line itself. However, at the time of this great traveler, they had not yet learned to accurately determine the value of this quantity. The first instruments, called inclinators, which made it possible to determine the angle of inclination of the Earth's magnetic field, were invented only more than half a century after the death of Columbus.
The first such design was proposed by the Englishman Robert Norman in 1576. But she turned out to be not entirely accurate in her testimony. Later, more advanced and sensitive inclinators were invented.
corner I between the geomagnetic field strength vector T and a horizontal plane at the point in question on the earth’s surface (see Terrestrial magnetism).n. m is measured from the horizontal plane up or down; N.m. is positive when the vector T directed downward from the horizontal plane, which is the case in the Northern Hemisphere, and negative when T directed upward - in the Southern Hemisphere. Nm varies on the earth's surface from 0° to ± 90°. Curves connecting points on the earth's surface with the same values of N.M. are called isoclines (See Isoclines). Isocline I= 0 is called the magnetic equator; point where I= 90°, - the north magnetic pole of the Earth; point where I= -90°, - the south magnetic pole (see Earth's magnetic poles). N.m. is measured using inclinators.
- - grammatical a category of a verb whose forms express differences in the relation of the content of the utterance to reality or in the relation of the speaker to the content of the utterance...
- - the angle between the geomagnetic intensity vector. fields and the horizontal plane at the considered point on the earth's surface...
Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
- - TILTING. A predicate form that denotes the speaker’s attitude to the reality of the manifestation of a feature expressed by a word or words with this form...
Dictionary of literary terms
- - the angle between the directions of a horizontal line and a magnetic needle, freely rotating on a horizontal axis and located in the plane of the magnetic meridian...
Technical railway dictionary
- - a quality that determines the opposite direction of modes and chords. Genetically the concept "N." intersects with ancient Greek. by origin the concept of "genus" ...
Music Encyclopedia
- - the angle between the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines and the horizontal plane. See Elements of terrestrial magnetism...
Geological encyclopedia
- - see Terrestrial magnetism...
Marine dictionary
- - the angle between the horizontal plane and the magnetic axis of a freely suspended needle...
Marine dictionary
- - special verb form; expresses one or another shade of the action signified by a given verb...
- - see Terrestrial magnetism...
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Euphron
- - I Mood is a grammatical category of a verb, expressing the relationship of the content of the statement to reality...
- - angle I between the geomagnetic field strength vector T and the horizontal plane at the considered point on the earth’s surface. n. m. is measured from the horizontal plane up or down...
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- - MAGNETIC Inclination - see Magnetic inclination...
- - in music - the quality of the mode, determined by which third is formed between the I and III degrees - major or minor. See Major and Minor...
Large encyclopedic dictionary
- - the angle between the vector of geomagnetic field strength and the horizontal plane at the considered point on the earth’s surface...
Large encyclopedic dictionary
- - the angle formed with the horizontal plane by a magnetic needle rotating around a horizontal axis in the plane of the magnetic meridian...
Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
"Magnetic inclination" in books
Magnetic magic
From the book What Einstein Told His Cook by Wolke RobertThe imperative mood in a call to the Other
From the book Personal Reality. Project coordination by Ananda AtmaThe imperative mood in a call to the Other “To start - and give up, and start again - and give up again, and always fight and rush about... But calmness is spiritual meanness!” “How the steel was tempered” “Start from the Beginning!” even in relation to oneself one must dose it so as not to
1.9, Magnetic intoxication.
From the book THE SCIENCE OF LOVE author Salas Sommer Dario1.9, Magnetic intoxication. Magnetic intoxication, being much less harmful and harmful than psychic vampirism, nevertheless turns a person into a blind creature, whose intelligence has faded, and the ability to think independently and make the right decisions
37. Magnetic field
From the book Medical Physics author Podkolzina Vera Alexandrovna37. Magnetic field A magnetic field is the name given to all matter through which force is exerted on moving electric charges placed in the field and on other bodies that have a magnetic moment. For a magnetic field, as well as for an electrostatic one,
Subjunctive mood
From the book The Tragedy of 1941. Causes of the disaster [anthology] author Morozov Andrey SergeevichSubjunctive Mood Again and again, historical consciousness returns to the question: was it possible to prevent the tragedy of the Soviet-German war? If Stalin had really tried to prevent war, what should he have done? Surround the country with lines of pillboxes
Chapter 1 THE SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD IN RUSSIAN HISTORY
From the book Father of Russian Cities. The real capital of Ancient Rus'. author Burovsky Andrey MikhailovichChapter 1 THE SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD IN RUSSIAN HISTORY That’s why I drink because I don’t understand Where the fate of events is taking us. S. Yesenin Perplexed questions Russian historians of the 19th century unanimously loved Novgorod as the cradle of popular rule. Just as unanimously, they almost did not notice Pskov, considering him
APPENDIX 2 Precession, true motion and inclination
From the book The Riddle of the Sphinx by Bauval RobertAPPENDIX 2 Precession, true motion and inclination Determination of the positions of the bright stars Regulus, Sirius and Al-Nitak in the distant past. Unlike the fixed values of latitude and longitude that cartographers use to indicate the position of objects on the map
Subjunctive mood
From the book Unknown Russia. A story that will surprise you author Uskov NikolaySubjunctive mood Once I thought: what would Russia look like if the revolution of 1917 had not happened in it? Well, first of all, the empire would have one more problem. According to preliminary agreements with the Entente, Russia was supposed to withdraw Constantinople. This is
Mood (in music)
TSBInclination (in music) Inclination in music, the quality of the mode, determined by which third is formed between the I and III degrees - major or minor. Hence there are two main types of scale: major (between the I and III degrees there is a major third) and minor. N. lada is associated with specific
Mood (grammatical category of verb)
From the book Great Soviet Encyclopedia (NA) by the author TSBMagnetic inclination
From the book Great Soviet Encyclopedia (NA) by the author TSBPelvic tilt
From the book Encyclopedia of Clinical Obstetrics author Drangoy Marina GennadievnaPelvic inclination This concept is due to the fact that when a woman is in an upright position, the upper edge of the symphysis is located below the sacral promontory, and the true conjugate forms an angle with the horizontal plane, the value of which is normally 55–60?. Pelvic tilt is called
IMPERATIVE MOOD
From the book Parkinson's Laws [How to succeed in work, play, and family life with the most modest abilities] author Parkinson Cyril NorthcoteIMPERATIVE Our ideas about power stem from the worship of the fathers, this is easy to prove: look at how we call our shrines in almost all languages. Young people remain dependent on their parents for quite a long time - this is the custom among people. Father is like that for us
IMPERATIVE MOOD OF HISTORY Instead of an afterword
From the book The Imperative Mood of History author Matveychev Oleg AnatolyevichIMPERATIVE MOOD OF HISTORY Instead of an afterword (Interview with Anatoly Belyakov with Oleg Matveychev) A.B.: I have long wanted to ask you, as a philosopher of a philosopher: what is philosophy? O.M.: Imagine that you are walking along a winding mountain path and don’t know what waiting around the corner:
Subjunctive Game
From the book Our Everything. Football Reader author Titov EgorGAME OF THE SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD - If you were the President of Russia? - Would you make the sport professional in all respects and make every effort to ensure that we dominate the world again. - ...Hippolytus from “The Irony of Fate”? - I would not wash in fur
At each point in space, the geomagnetic field is characterized by a strength vector N, the magnitude and direction of which depend on the coordinates of a point on the Earth’s surface. The geomagnetic field strength decreases from the magnetic poles to the magnetic equator from ~53 A×m-1 to ~28 A×m-1, average value N at the surface is ~45A×m-1, and at the boundary of the magnetosphere ~10-3A m-1. The Earth's dipole magnetic moment forms an angle q = 11.5° with the Earth's rotation axis. Geomagnetic field magnitude N consists of a constant and variable component. The constant component is determined by the internal structure of the Earth and is subject to slow changes, its contribution to the full value N is 99%. In different geological epochs, the geomagnetic field had different polarities, that is, with a period of up to 10 million years, a reversal of the Earth’s main magnetic field occurred. Paleomagnetic studies have shown that the last such change took place about 700 thousand years ago. The variable component of the geomagnetic field (its contribution to N is 1%) is caused by electric currents in the magnetosphere associated with the flow around and breakthrough of the solar wind, which has different densities and velocities of charged particles. Periodic solar-diurnal and lunar-diurnal magnetic variations are observed N, as well as strong disturbances of the magnetosphere - magnetic storms,
accompanied by auroras, ionospheric changes, and the appearance of X-ray and low-frequency radiation. Magnitude and direction of the tension vector N depend on the coordinates of the point in the magnetosphere at which this quantity is determined. At any point, the vector of the earth's magnetic field strength N can be decomposed into components (see Fig. 2). Tension vector direction N coincides with the tangent to the field line
Earth's magnetic field and at the magnetic equator horizontal to the surface, and at the magnetic pole - vertically. At points where the horizontal component N g disappears, the magnetic needle is set vertically. These points are called poles of magnetic inclination(magnetic poles). At any other points of the magnetosphere, the intensity vector N directed at an angle b to the vertical at a given point on the Earth (see Fig. 2). Angle b between the direction of the vector N at a given point in the magnetosphere and the horizontal plane is called magnetic inclination(Fig. 2). Due to the mismatch of magnetic and geographical
The physical poles do not coincide and the planes of the magnetic and geographical meridians do not coincide.
Angle b between the directions of magnetic and geographic me-
rhidians at a given point in the magnetosphere is called magnetic
declination(Fig. 2). To observe the temporary directions of the magnetic and geographic meridians at a given point magnetic. To observe the time directions of the magnetic and geographic meridians at a given point in the magnetosphere, it is called the magnetic variation of the declination value (and to carry out surveying and geophysical measurements), a declinator device is used (declino (Latin), deklinativ (English) - deviation).
Full vector of tension N geomagnetic field at any point in the magnetosphere can be decomposed into two components: horizontal Ng and vertical Nv(see Fig. 2). A detailed study of the Earth's magnetic field has important scientific and practical significance and comes down to the systematic determination of changes in the elements of the magnetosphere (a, b, Ng) in various geographical locations. The elements of terrestrial magnetism for Greenwich in 1955 had the following meanings:
a =80.44" W, b =660.33", Hg = 0.187, Hv = 0.434. The geophysical station closest to Irkutsk, located in the village. Cartridges, has geographic coordinates: 52.470C, 104.030V, geomagnetic
coordinates: 41.6.0 174.750. The elements of Earth's magnetism according to the data of this station for Irkutsk in 1980 had the values a = - 2.360, Bg = 19.65 10 -6 T, Bw = 59.9 10 -6 T.
For a number of successive epochs, usually every five years, the distribution of the magnetic field on the Earth's surface appears magnetic cards three or more magnetic elements. On such cards there are isolines, along which this element has a constant value. Lines of equal declination a are called isogons, moods b - isoclines, the magnitude of the total tension vector H - isodynamic lines
(isodynamics). On the maps N with isodynamics foci, where H=0, and there are magnetic poles(inclination poles). These poles (like geographic poles) are the points of convergence of isogons on maps of equal declination a.