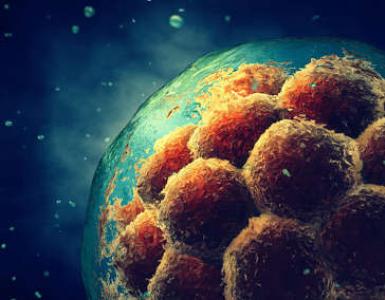
What is biochemical pregnancy and how does it affect a woman’s health? What you need to know about biochemical pregnancy Can a biochemical pregnancy develop into a normal one?
Biochemical pregnancy after IVF - what is it and its causes
Successful fertilization of eggs does not guarantee pregnancy. Only 30-40% of embryo transfers in in vitro fertilization protocols are successful. This suggests that biochemical pregnancy after IVF() occurs quite often. BxB is a condition in which a woman’s hormonal background changes to the same as with, but the pregnancy is terminated in the near future, and menstruation begins.
Biochemical pregnancy - what is it?
In women who do not undergo the IVF procedure, chemical pregnancy develops in 70% of cases. In this case, signs of pregnancy are determined only by the result.
Preparation for the new protocol after BCB
After completing IVF with a biochemical pregnancy, you can enter into the next protocol no earlier than 3 months later. provides information about the need for a more in-depth examination and preparation for a new procedure.
To exclude genetic abnormalities, they carry out. In this case, a biopsy of one blastomere is taken from a 5-day embryo. PCR diagnostics makes it possible to determine chromosomal rearrangements and inherited genetic diseases in married couples who are carriers of monogenic diseases. The following can be diagnosed:
- cystic fibrosis;
- hemophilia A;
- sickle cell anemia;
- Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome.
If the cause of protocol failure is an autoimmune factor, it. It detects sperm bound by antisperm antibodies, which act as a male factor in infertility.
Diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome includes the determination of various types of antibodies:
- antiphospholipid;
- lupus anticoagulant;
- AT to cardiolipin – IgM, IgG;
- antithrombin III;
- Ig A, M, G to beta-2-glycoprotein.
Blood coagulation indicators obtained from a coagulogram will eliminate the tendency to thrombus formation.
To increase the chances of pregnancy, cryopreserved blastocysts are subjected to dissection of the outer membrane.

Cryotransfer of a thawed embryo can occur in or. Tactics are determined by a fertility specialist on an individual basis, depending on the data obtained during the examination.
Replanting in the natural cycle has a number of advantages:
- there is no likelihood of ovarian hyperstimulation;
- the receptive properties of the endometrium are better;
- less risk and later.
A stimulated cycle is necessary for luteal phase deficiency. It is carried out with progesterone and its analogues. If there is no risk of development, hCG may be used.
Pregnancy has a lot of mysteries that scientists are still pondering. In the 21st century, they continue to look for the causes of the so-called biochemical pregnancy - the name was invented, the process was described, but it is difficult to clearly answer the question “in what cases does it occur?” But for a woman who wants to give birth to a child, even incomplete information about how conception can turn out to be useful.
"A little pregnant"
In gynecology, biochemical pregnancy is a pregnancy that spontaneously terminates within 4–6 weeks after conception. The term seems strange at first glance; most likely, it arose because at such early stages pregnancy is determined only by the level of a certain hormone - that is, by a chemical indicator.
Doctors say that every sexually active woman has experienced a biochemical pregnancy at least once in her life, and on average, three out of four conceptions end in it.
Mechanism of early miscarriage
After fertilization, the egg, continuously dividing, moves through the fallopian tubes into the cavity of the reproductive organ. Once in the uterus, after 3-4 days the unborn baby, already in the form of a fertilized egg, is ready to perform the next task - to attach to the endometrium, or the mucous membrane lining the walls of the organ. It is implantation that is the decisive moment on which it depends whether a new person will be born. Attachment is not a quick process, it lasts about two days.
The first “exam” for the embryo: the task is to attach to the uterine mucosa; Once attached, it means you survived
If the embryo manages to attach to the endometrium, menstruation usually stops, since immediately after conception a temporary organ appears in the woman’s ovary - the corpus luteum, which produces the “pregnancy hormone” - progesterone. It stimulates the growth of the endometrium and, when the embryo is successfully implanted, “slows down” menstruation.
But often at this stage a failure occurs: for some reason the process of embryo implantation is disrupted. Meanwhile, the work of the endometrium depends entirely on hormonal processes. If the baby is not attached, the brain does not receive a signal to synthesize the necessary hormones; As a result, before the onset of menstruation, endometrial detachment begins. Part of the mucous membrane lining the uterus is rejected and washed out of the body with bleeding, carrying with it the embryo, which has nothing to cling to. There is a biochemical pregnancy.
The World Health Organization classifies a biochemical pregnancy as the death of the fetus - despite the fact that the rejected embryo has not even begun to show signs of a living being.
How does a failed mother feel?
As a rule, almost nothing. The embryo leaves the body too early, even before the first symptoms of pregnancy appear. In rare cases, a woman exhibits the following signs:
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- heightened sense of smell;
- discharge.
The signs are not too bright, so they go unnoticed by most. Like the biochemical pregnancy itself, which a woman most often does not even know about, although conception has occurred, and then a miscarriage. Moreover, bleeding as a result of the expulsion of the embryo almost coincides with the next menstruation.
Only ladies who are very attentive to their health will be wary because:
- menstruation was “late” by 5–7 days;
- excessive bleeding, clots of mucus are noticeable in the blood;
- menstruation is accompanied by pain, sometimes severe.
Each of these signs indicates that the pregnancy has already been terminated.
A slight delay and pain during menstruation are indirect signs of biochemical pregnancy
How to detect pregnancy in the first weeks
Those women who have been trying to get pregnant for a long time measure their basal temperature daily (the thermometer is placed in the rectum or vagina for 3-5 minutes). When such a temperature rises from 36.7 to 37 degrees, this is already a sign of pregnancy, the very first and, of course, controversial - the rise is too insignificant. But if the temperature lasts for two weeks, the chances of a successful conception increase. When the basal temperature returns to normal, most likely the fetus has not implanted and the pregnancy has been terminated. This will be confirmed by menstruation.
Electronic pregnancy tests are considered the most sensitive (they are more accurate than test strips). Use from the first day of the delay. The device reacts to even slight changes in hormonal levels, moreover, it determines the period that has passed since conception. Alas, electronics also make mistakes, so you cannot rely on the test result.
In the first weeks of pregnancy, even an electronic test sometimes gives a false result, although it is considered the most accurate
And a regular urine test in the early stages will not detect pregnancy.
Ultrasound examination is also useless - the embryo is too small to appear on the monitor screen.
When will a hCG test help?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a sex hormone of a protein nature that is synthesized by the body during changes in the reproductive system. In adult women, the level of hCG does not exceed 5 mIU/ml, where IU is a unit of measurement of the amount of substances accepted in pharmacology, depending on their biological effect.
When pregnancy occurs, the level of hCG in the blood increases - twice every two days. It is clear that eventually the hormone will end up in the urine, but later - that is why it is so unreliable to determine pregnancy by the composition of urine, including using electronic tests.
Another thing is a blood test for hCG: it will confirm conception within 7–10 days. If a woman can’t wait to find out whether she’s pregnant or not, there’s no better option. Blood is donated:
- from a vein;
- since morning;
- on an empty stomach;
- refusing to take medications two days before the procedure.
True, if a woman takes hormonal drugs, doctors cannot vouch for the accuracy of the result.
HCG is a hormone that makes no mistakes; if its level in the blood is elevated, the woman is pregnant
After the onset of heavy menstruation, a woman goes to the clinic for clarification - the doctor will probably suspect a biochemical pregnancy; a blood test taken again to be sure will show a decrease in the hCG level to standard values.
Well, in the case of a steadily growing hCG, pregnancy develops normally; if later it is still interrupted, it is no longer considered biochemical - the gynecologist ascertains a normal miscarriage.
Why does biochemical pregnancy occur?
Doctors argue about the reasons for the sudden interruption of embryonic development in the early stages; the identified factors are not enough to explain such a high percentage of embryo deaths. Clinical studies are complicated by the transience of what is happening and the hidden nature of biochemical pregnancy.
Objective reasons
So far it has been proven that the embryo does not attach to the endometrium because:
- the woman has immune disorders; with the beginning of a normal pregnancy, the expectant mother’s immunity is suppressed for natural reasons - nature seems to save the fetus from the mother’s antibodies, which mistake the new organism for a foreign object and try to get rid of it; if the immune cells are still active, the embryo has a hard time; it is unable to defend itself from the “aggressors” and dies;
- there was a hormonal imbalance in the female body; Thus, sometimes low levels of progesterone are diagnosed, which is responsible for attaching the fetus to the mucous membrane and reduces too intense contractions of the uterus;
- a woman has a severe blood disease - for example, thrombophilia (blood clotting disorder, blood clots); due to slow blood flow, the embryo does not receive enough nutrients, which ends in its death;
- iron deficiency anemia develops - the same story: iron is part of hemoglobin - a protein involved in the transfer of oxygen; lack of iron - hemoglobin level is reduced - the embryo does not receive enough oxygen;
- there are congenital anomalies in the structure of the reproductive organs that interfere with the implantation of the fertilized egg;
- the development of the trophoblast, the outer layer of cells from which the placenta is subsequently formed, is disrupted in the embryo;
- already at the stage of cell division, the embryo developed developmental anomalies incompatible with life, obtained with the genes of one of the parents or both at once; the occurrence of a chromosome defect is possible at different times, but there are critical moments, for example, the first three days after conception, when the egg divides due to its own genetic material; nature seems to weed out the “wrong option”, not allowing the “defective” embryo to develop further - so to speak, natural selection in action.
Low progesterone in a woman, in turn, is provoked by the following factors:
- abortions that ended previous pregnancies;
- renal failure;
- pelvic organ infections;
- malignant tumors;
- taking certain medications.
By the way, increased levels of the hormone also threaten early pregnancy failure; Often women are prescribed drugs with progesterone; if the dosage is not observed, the amount of the hormone reaches values dangerous for pregnancy.
Subjective reasons
With a high degree of probability, biochemical pregnancy awaits women who:

According to some doctors, spontaneous miscarriage in the first weeks of gestation occurs due to poor nutrition. A diet in which the amount of protein is reduced and the sugar content is increased interferes with the normal development of the embryo. Fast food rich in carbohydrates is also harmful to the expectant mother. However, we recognize that such reasons, if they influence termination of pregnancy in the first weeks, do so indirectly, in combination with other factors.
Fast food is the worst enemy of pregnant women, but the girl may not be aware that she is already pregnant
A strict diet to which a woman dissatisfied with her figure subjects herself is also dangerous; such a woman may not even know that she became pregnant, and the unborn child turns out to be doomed. It is not for nothing that dry fasting (without food and water) is considered an effective way to terminate pregnancy at the very beginning.
If a lady is interested in traditional medicine and decides to be treated with strong herbal decoctions, the embryo will also have a hard time; most likely to be poisoned.
Consequences of biochemical pregnancy
Those who did not even feel the symptoms of a disruption in the pregnancy process are unlikely to find out that they were “a little pregnant.” Women who experience abdominal pain after an early miscarriage are likely to see a doctor. But even in this case, detecting a biochemical pregnancy is problematic - only a hCG test taken before bleeding will indicate it.
It is impossible to save an embryo, which, as they say, is “destined” to be expelled from the body. They haven’t come up with such a method - so what’s there to talk about, even if diagnosing a biochemical pregnancy is still difficult. Taking hormonal medications under the supervision of a doctor will only help the implantation of the embryo during the next pregnancy.
How to be treated
Spontaneous abortion in the first weeks usually occurs without negative health consequences; along with the fertilized egg, part of the endometrium also leaves the uterus, so the woman avoids the unpleasant curettage procedure. The body cleanses itself and does not require medical intervention. Even antibiotics are not required.
However, just in case you suspect you were pregnant, ask your doctor to examine you. When the pregnancy has reached 10 weeks, and the fetus has grown to 3 centimeters, it may still be necessary to treat the uterus.
Well, of course, you cannot do without treating the pathologies that provoked miscarriage. So, a woman is sometimes prescribed a course of treatment with hormones so that the body is prepared for conception better than the last time. Intramuscular injections or vaginal suppositories with progesterone will help avoid fiasco.
It’s sad when a woman finds out about the pregnancy she wanted, and then has a mini-miscarriage. In such cases, of course, the support of relatives is required, and sometimes the help of a psychologist; The main thing is to calm the girl down, explain that this did not happen to her alone and will still happen.
For some, biochemical pregnancy does not pass without a trace; woman is depressed and needs psychological support
Karyotyping of spouses
When trying unsuccessfully to conceive a child, a woman believes that she or her partner is infertile; in fact, the lady’s pregnancies are terminated one after another at very early stages, but the failed mother has no idea about it.
Karyotyping is a new research method that allows you to study the full set of patient chromosomes (karyotype). With a high degree of accuracy, the test will show the compatibility of future parents at the gene level, which means the likelihood of conceiving a baby with congenital chromosomal abnormalities. Perhaps the “war of genes” between a man and a woman caused the early rejection of the embryo, which, due to genetic defects, was not adapted to normal life outside the womb.
Human karyotype - 23 pairs of chromosomes; the specialist must make sure that there is no extra chromosome or part thereof in any of the pairs
The karyotype test is serious and requires two weeks of preparation. Both donate blood from a vein, on an empty stomach. Laboratory technicians examine the biomaterial for several days. First of all, doctors advise couples wishing to have a child to undergo karyotyping when:
- one of the partners is over 35 years old;
- one of the two in the family had genetic diseases;
- one or both worked in hazardous industries and were exposed to radioactive radiation;
- one or both are addicted to bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, using drugs);
- The expectant mother had a number of unsuccessful IVF attempts.
If necessary, the doctor will send the spouses for additional examinations, for example:
- a man - for a MAP test, which will detect unwanted antibodies in sperm;
- a woman - for antibody analysis;
- a woman - for a coagulogram, which examines the level of blood clotting.
When to try again
Biochemical pregnancy is not classified by doctors as a disease. Sometimes a woman is upset, depressed, in rare cases there is an emotional shock that leads to depression - in such cases it is necessary to wait until mental health is restored.
But the reproductive organs are practically not affected, so there is no need to delay a new conception. In addition, the probability of repeated failure is low - otherwise humanity would have long ago faced a demographic catastrophe.
Some doctors recommend trying again in the next menstrual cycle, others advise giving the woman a break and waiting three or four cycles. With the onset of a new pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to listen sensitively to her body and monitor the development of the baby.
Biochemical pregnancy and IVF
In vitro fertilization is a chance for a childless couple to have offspring. It is curious that it was the introduction into practice of this and similar methods that introduced the term “biochemical pregnancy” into medical use.
The fact is that during IVF, doctors carefully monitor the development of the egg implanted in the female body and monitor whether the embryo has attached to the endometrium. Two weeks after the procedure, the woman takes an hCG test: doctors already know for sure whether pregnancy has occurred. From this moment on, the patient’s blood is examined every 2–3 days to ensure the normal development of the embryo or to detect a spontaneous abortion.
It is thanks to the close attention of medical personnel that not a single case of biochemical pregnancy goes unnoticed; therefore, for patients who decide to undergo IVF, the percentage of mini-miscarriages is much higher than for those who went through natural fertilization - it’s just that the clinic keeps statistics of failures.
However, doctors do not have a consensus on the degree of influence of IVF on the risk of embryo rejection. Thus, a number of doctors suggest that biochemical pregnancy is still provoked by the following factors:
- ovarian hyperstimulation, which is performed to obtain an egg;
- hormonal medications that are given to the patient before the IVF procedure; As a result, the balance of hormones is lost;
- nervous tension in a woman, sometimes turning into stress; It is clear that she is worried about the outcome of the operation.
And yet, such hypotheses have not received scientific confirmation.
According to statistics, the embryo takes root the first time on average in every third or fourth patient; the result depends on the chosen replanting method. The second attempt, as a rule, is much more successful - up to 40% of women state that they did not spend their money in vain.
Negative experience is also experience; after failure, the body seems to adjust to pregnancy, it has “rehearsed” the process and is ready to try again. In this case, another IVF is possible:
- if frozen eggs are used (so-called cryotransfer), already in the next menstrual cycle;
- if doctors prefer ovarian stimulation and follicle puncture, wait up to three cycles.
Often, after stimulation, the doctor advises the spouses to try to conceive a child naturally; sometimes it works.
After a series of failures, the couple will have to undergo examination: tests for karyotype, antibodies, and others.
How to avoid embryo rejection
Biochemical pregnancy in most cases is like a natural disaster; impossible to prevent. However, since there are subjective reasons for miscarriage, it makes sense for a woman to at least reduce the risks.
Try:
- visit a gynecologist regularly;
- avoid infectious infections of the genitals and urinary tract;
- be less nervous;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- leave smoking, drinking and other harmful addictions in the past;
- include protein-rich foods in your diet, give up excessive amounts of sweets; fruits, vegetables, grains, as well as high-quality oil and fish dishes - this is your menu when you are planning to conceive a child.
Refusal of flour and sweets in favor of salads in some cases will reduce the risk of miscarriage
One of the insufficiently studied stages of pregnancy is the process of fertilization of a mature egg, starting from its meeting with the most active sperm and ending with the consolidation of the embryo in the uterine cavity. If for some reason this does not happen, then the pregnancy is terminated, and this condition in medical practice is called biochemical pregnancy. This process is determined only by biochemical analysis.
According to medical statistics, at least 65% of all pregnancies, regardless of one reason or another, end in the early stages, when the woman is not yet aware of her interesting situation, and bleeding as a result of spontaneous abortion is perceived as another menstruation.
In gynecology, there has long been such a term as biochemical pregnancy, the essence of which is that the fertilized egg does not have time to attach to the walls of the uterus and the pregnancy is terminated with the onset of menstruation. Unlike ordinary critical days, this process is manifested by severe pain and more profuse bleeding, but does not cause any special concern on the part of the woman. Well, those who dream of purposefully conceiving a baby and wait weekly for the first signs of toxicosis and fatigue to appear may not see their pregnancy.
The insidiousness of biochemical pregnancy is that it begins with a delay in menstruation, but this is not displayed on an ultrasound or in the results of a pregnancy test. Impatient to find out the reason for the delay, the woman takes a test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin hormone), which confirms her situation, only after a couple of days the scheduled menstruation occurs. This is called biochemical pregnancy, the nature of which is very difficult to explain.
Biochemical pregnancy always ends in spontaneous abortion, and a young couple who wants to conceive and give birth to a healthy child should find out why this happens, what are the reasons that the embryo cannot implant in the uterus. A new pregnancy can be planned from a new cycle, however, in order to avoid the unpleasant situation from happening again, you need to see a doctor, consult, be examined and, if necessary, begin treatment.
Causes of biochemical pregnancy
It is impossible to accurately determine the factor that provoked a biochemical pregnancy, and only after a long examination and analysis of the health status of the man and woman will the doctor be able to name the probable cause of the failure. It could be:
- failure in a woman’s hormonal system;
- changes in chromosome structure;
- immune and autoimmune disorders;
- thrombophilia and other blood diseases.
The concept of “treatment” in this case means eliminating the causes that provoke the appearance of biochemical pregnancy, because there are women who have repeatedly suffered this condition and here we are talking about miscarriage.
The fact of spontaneous abortion is not a consequence of problems with female fertility; after a biochemical pregnancy, uterine curettage or medication treatment is also not required. At this early stage of its development, the embryo is removed during menstruation along with menstrual bleeding.
Symptoms of biochemical pregnancy
Like a normal pregnancy, a biochemical pregnancy makes itself felt by a slight delay in menstruation. There are no symptoms such as pain in the mammary glands, nausea, drowsiness or fatigue. Women for whom pregnancy was not planned may not even notice any special sensations and quite calmly accept small deviations from the schedule. Those who are expecting pregnancy listen more carefully to the voice of the body and can determine their biochemical state. Its ghostly signs include:
- several days of delay in menstruation;
- heavy bleeding, not as usual;
- painful menstruation.

HCG and biochemical pregnancy
There are often cases when fertilization has taken place and does not provoke the appearance of various symptoms at all, then an accurate diagnosis in the early stages will help to make a certain medical analysis, namely hCG for biochemical pregnancy.
As is known, the level of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood increases with the onset of pregnancy even before the delay of menstruation. At this stage, even an ultrasound cannot discern an interesting position, while hCG is able to show the result.
An analysis with a mark of 5 mU/ml can indicate the fact of the onset of biochemical pregnancy. If an ultrasound examination and gynecological examination do not confirm the fact of embryo development, and a repeated blood test shows a sharp decrease in the concentration of the hormone, then we can assume that a so-called biochemical pregnancy has occurred. If, with high chorion levels on an ultrasound, the doctor discovers the remains of the fertilized egg in the uterus, and the woman begins to feel noticeable changes in her health, it means that a normal pregnancy has occurred.
Planning a new conception
Many women often ask when they can plan a new pregnancy after a biochemical pregnancy. According to doctors, conception can be carried out already in a new cycle, and there is a high probability that with a new attempt the woman will successfully become pregnant and also give birth to a healthy child.
In fact, biochemical pregnancy is not a death sentence, as many women think. If your first attempt was unsuccessful, then it is not a fact that the second will be repeated in the same way. A full examination and treatment will be needed if failures occur over and over again. Moreover, both the woman and the man must be examined so that the doctor can determine the probable cause of miscarriage. Most often, a gynecologist selects a course of hormone therapy for a woman to avoid the occurrence of a biochemical pregnancy and prepare her body for fertilization.
The IVF artificial insemination method is widely used in medicine today, giving infertile couples a chance to successfully conceive and become parents of a healthy baby. If we talk about biochemical pregnancy, women should know that after IVF the percentage of spontaneous abortion is much higher than in conditions of natural fertilization. If a miscarriage occurs after a medical procedure, then the next course of IVF should be repeated no earlier than after 2-3 months. These terms depend on the patient’s health condition and her body’s reaction to laboratory manipulation.
In this case, it is necessary to consult a qualified specialist who can help the woman reduce the risk of biochemical pregnancy, successfully become pregnant through IVF and carry the child to term.

Biochemical screening and its necessity
The term “biochemical screening” must be understood as a set of specific diagnostic procedures aimed at identifying factors that can lead to spontaneous abortion. Being an important component of comprehensive prenatal screening (ultrasound and laboratory tests), biochemical is absolutely safe for health and does not have a harmful effect on pregnancy and the developing fetus. The purpose of its implementation is to search for the risks of having a child with chromosomal abnormalities and severe defects in the development of the neural tube.
Biochemical screening during pregnancy is carried out in two stages:
- first trimester study - double test from 10 to 14 weeks;
- second trimester study - triple test from 16 to 20 weeks.
In addition to identifying possible chromosomal pathologies, screening is also carried out in such cases when:
- partners are blood relatives;
- the woman suffered a frozen pregnancy;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- first child with a chromosomal abnormality;
- high probability of spontaneous abortion;
- there has already been a case of biochemical pregnancy;
- immediately before pregnancy, the woman suffered a viral or bacterial pathology;
- radiation therapy given to one of the partners shortly before conception.
A study of the blood of a pregnant woman makes it possible to identify pathologies such as Down syndrome, neural tube defects of the fetus, malformations, and trisomy. In order to successfully and efficiently undergo this procedure, a woman must follow a number of medical instructions regarding nutrition.
Before the analysis, you should not eat citrus fruits, spicy, fatty and fried foods, smoked foods and chocolate. Screening is best done in the morning on an empty stomach; if you are thirsty, you can drink still water no later than four hours before the test. It is necessary to donate blood for biochemistry together with the results of ultrasound screening. In laboratory conditions, venous blood is collected, after which the results of the study will be ready in no less than 1.5 weeks.
Biochemical diagnostics of the first trimester allows you to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and PAPP-a protein. For example, if, as a result of the analysis, your indicator was 0.5 - 2.5 MoM (arbitrary units), then everything is in order with the level of hormones. A value of less than 0.5 MoM is considered low, and a value of more than 2.5 is considered high, respectively.
After biochemical screening of the 1st and 2nd trimester, a special analytical program calculates the risks of the appearance of certain syndromes. The calculation results can be largely influenced by the following factors:
- overweight and underweight of the patient;
- pregnancy as a result of artificial insemination;
- laboratory testing of amniotic fluid has recently been carried out;
- multiple pregnancy;
- diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman.
As a result, the risks for each pathology are entered into a separate table. A value of 1:380 or more is considered high. Average – 1:1000. Low – 1:10000. The number after the colon means that, for example, out of 10 thousand pregnant women with this hCG level, only one will have a child with Down syndrome.

Diet and biochemical pregnancy
We are what we eat and it is impossible to disagree with this statement, because in fact, almost all diseases that overtake a person, in most cases, were provoked by poor-quality nutrition.
In the case of biochemical pregnancy, it’s almost the same. Doctors say that it is quite possible to influence the process of egg release and its quality with the help of a special diet. In order to reduce the likelihood of spontaneous abortion after IVF, experts recommend consuming protein in large quantities, that is, following a hyperprotein diet.

The ability to successfully get pregnant is directly influenced by the amount of protein in the diet and vice versa, if this component is not enough, this will definitely lead to problems with fertilization. Excess sugar in the body interferes with getting pregnant, as a result of which the in vitro fertilization procedure may simply be ineffective, which will lead to a biochemical pregnancy. Fast food and other refined foods reduce the body's sensitivity to insulin, and this in turn slows down the process of follicle maturation and egg release.
The results of numerous medical studies have led to the fact that the predominance of fish, vegetables, fruits and high-quality oils in the diet of the expectant mother contributes to the successful implementation of IVF. And to achieve high results, such a diet should be followed approximately three months before the IVF protocol.
When planning a new pregnancy after undergoing a biochemical pregnancy, you need to carefully monitor your health, menstrual cycle, nutrition, daily and sleep patterns. Examinations by a gynecologist should be regular, and infectious diseases should be treated in a timely manner.
Biochemical pregnancy. Video
Which occurred during a period when the embryo cannot yet be seen on an ultrasound, but can be determined by a blood test or pregnancy test. This may be great news for some people, but not so much for others. It is said to occur when you test positive on a pregnancy test, but your period occurs a few days later. When this happens, most women don't even know about it. But among the rest, many are left feeling empty and confused, especially as they look forward to a new addition to their family.
Often, a biochemical pregnancy is simply mistaken for a false pregnancy test. However, in fact, in this case you have a very early miscarriage.
What does biochemical pregnancy mean?
Simply put, it is a clinical term used to refer to very early miscarriage. It occurs too early, even before ultrasound can detect a heartbeat (this is possible after the 5th week). A chemical pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg does not attach to the wall of the uterus. It is quite common and occurs more often than half of women's first pregnancies. But it often goes unnoticed and is mistaken for later menstruation. However, it can be detected using many highly sensitive pregnancy tests available today.
What are the signs and symptoms?
Some women may not even know they are pregnant and therefore may not know whether a chemical pregnancy has occurred. This makes it difficult to clearly determine the number of cases of this condition. Women who are trying to conceive and track their cycles and ovulation may notice when this happens.
Possible symptoms:
- Scanty discharge during menstruation
- Late menstruation
- Positive pregnancy test
- Abdominal cramps
- Decreased hCG levels in the blood.
Why does biochemical pregnancy occur?
There are many reasons for its occurrence. These include low hormone levels, insufficient thickness of the uterine lining, infections and luteal phase defects. However, the most common reason suggested is that chemical pregnancies occur due to chromosomal problems in the developing embryo. This occurs as a result of poor egg or sperm quality, abnormal cell division in the embryo, or genetic abnormalities in either partner. We can say that the body thus prevents the gestation of an unhealthy fetus.
How is it diagnosed?
Biochemical pregnancy can be diagnosed using blood tests. Your doctor will monitor your human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels throughout your pregnancy to make sure it is progressing normally and there is no risk of miscarriage. If the level of this hormone drops sharply, a miscarriage is likely to occur. An hCG test is done to diagnose biochemical pregnancy. You will also likely have an ultrasound after your tests. An ultrasound can detect any signs of life in your womb. In a chemical pregnancy, no heartbeat can be detected and implantation cannot be visible.
How to cope with a biochemical pregnancy?
1. Physical recovery will not take too long
As noted earlier, in this condition, miscarriage occurs early and therefore has little impact on the woman's body. It is mainly mistaken for the late onset of menstruation. However, after a chemical pregnancy, bleeding is less heavy than usual. It may also be accompanied by cramps, but recovery occurs quickly.
2. It's okay to feel upset.
Most women never find out that they have had a very early miscarriage. However, with the availability of highly sensitive pregnancy tests, it is possible to know when a chemical pregnancy occurs. Finding out that you've suffered a miscarriage can be devastating, especially if you were looking forward to the birth of your baby. If you are experiencing feelings of grief over a loss, you can seek help from support groups or your partner. You can also talk to your family and close friends. This can greatly help you get through this period.
3. Get treatment if necessary
Because most chemical pregnancies go undetected, very few people actually undergo treatment. It is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle and you can have children in the future, even without receiving treatment after a biochemical pregnancy. If you are at risk for this condition, you may want to seek help from your doctor to monitor your hCG levels. If it doesn't decrease, you most likely won't have a miscarriage, which can lead to health complications. Your doctor should monitor your condition closely for several months after a chemical pregnancy.
4. Prepare for another pregnancy
You can get pregnant immediately after a biochemical pregnancy. There is no medical problem that prevents you from conceiving again. It does not affect a woman's fertility and ovulation continues as usual. In addition, the next cycle may be longer than the previous one.
There is actually no way to prevent chemical pregnancy. This is due to the fact that its causes are beyond our control. Most are caused by genetic problems in the embryo and therefore cannot be prevented. However, minor lifestyle changes can help prevent any potential miscarriages in the future. Eating healthy and avoiding the use of any drugs can help maintain a healthy pregnancy.
(1 ratings, average: 5,00 out of 5)
Fertilization of the egg, its movement from the fallopian tube to the uterus and implantation are the initial and, at the same time, the least studied stages of pregnancy. If any of them fails, spontaneous abortion occurs. In this case, we will be talking about such a phenomenon as biochemical pregnancy.
Most often, a woman does not know that conception and natural expulsion of the fertilized egg have occurred. Bleeding practically coincides with the next menstruation and does not cause concern. According to statistics, about 70-75% of all pregnancies are biochemical.
A biochemical pregnancy begins in the same way as a normal one: the egg is fertilized by a sperm, descends into the uterus, and sometimes even attaches to its wall. But closer to the beginning of the next menstrual cycle, the process of embryo development occurs.
Those women who are not planning a child or are focused on the appearance of menstruation on time do not know that conception and miscarriage have occurred. Menstruation after a biochemical pregnancy is practically no different from normal menstrual flow. They may be a little more abundant or more painful, but, in general, they are the same.
The situation is different with those women who really want to become mothers and have been trying to get pregnant for a long time. They are attentive to any changes in their well-being, especially in the second phase of the cycle; many keep a graph of basal temperature. In such a situation, the onset of conception does not go unnoticed.
In some cases, electronic (highly sensitive) tests for determining the concentration of hCG in urine can give a positive result. On the basal temperature chart, an interruption may be reflected by a decrease in readings. But more reliable examination methods, such as ultrasound, will not yet determine pregnancy. And in a few days menstruation will come.
Symptoms
Often, biochemical pregnancy is asymptomatic, so in most women it goes unnoticed. symptoms that can be observed during normal pregnancy, such as swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands, changes in taste habits, increased sense of smell, drowsiness, irritability, are usually absent.
Biochemical pregnancy has its own signs that few women notice, since these manifestations are barely detectable and very subjective.
Those who are well aware of the state of their body and know about the characteristic changes in each phase of the cycle can pay attention to:
- slight delay in menstruation (up to 5-7 days);
- more severe pain during bleeding;
- more intense discharge.

Thus, if biochemical pregnancy is determined, it is only after its completion. Symptoms indicate spontaneous abortion, and not the fact of conception and development of the embryo.
Causes
The causes of biochemical pregnancy are varied and their list is still growing. The most likely influence of the following factors:
- the presence of immune and autoimmune disorders in a woman, which lead to rejection of the fertilized egg as a foreign agent;
- the presence of hormonal disorders, for example, insufficient production of progesterone, a hormone that promotes and reduces the contractility of the uterus;
- the presence of blood diseases in a woman;
- genetic abnormalities of the fetus incompatible with life, which can be transmitted from both the father and the mother.
The need to determine the causes of biochemical pregnancy exists only if it recurs frequently, the couple cannot have a child for a long time and there is a suspicion of infertility. In this case, the doctor sends the woman for a full examination, and both spouses for a karyotype study.
HCG during biochemical pregnancy
The beginning of any pregnancy is accompanied by an increase in hCG levels. This hormone is produced by chorionic cells and indicates implantation even before it can be confirmed by ultrasound.
Biochemical pregnancy is no exception: when it occurs, the concentration of hCG in the blood exceeds 5 mIU/ml and doubles every 2 days. This hormone appears in urine later, before the onset of menstruation. Therefore, home tests may not have time to “catch” its peak.
But if a woman donates blood for a test before the expected start of menstruation, she will receive a positive result, which can be used to determine the date of conception. Repeat testing usually indicates a decrease in hCG to the usual level (5 mIU/ml). The doctor concludes that the biochemical pregnancy is completed.

If a repeated laboratory blood test indicates an increase in the concentration of hCG and after some time the presence of a fertilized egg is confirmed by ultrasound, then the pregnancy is considered normal. Interruption at a later date also does not make it biochemical.
Is treatment necessary?
Biochemical pregnancy is not a disease. Therefore, there is no need to treat it. A miscarriage at such an early stage occurs without complications and does not require medical care (medication, diarrhea, aspiration, etc.). The reproductive system recovers independently and quickly.
But when early interruption occurs repeatedly, it is necessary to think about eliminating the causes that cause it. First you will need to undergo a series of examinations, and then treatment.
In some cases, it is impossible to restore health and get rid of infertility. Then the question of carrying out the procedure is decided