New information technologies. Apparat - Magazine about the new society
The future of the IT industry in 2017 will be determined by artificial intelligence, “smart” things, virtual and augmented reality and blockchain, and advanced technology platforms for business. Such conclusions were made by experts of the Gartner research company at the ITxpo-2016 symposium, which was held in Orlando. The correspondent of the Teplitsa Social Technologies translated an article about the 10 main technologies of the future.
According to Gartner Vice President David Cearley, these 10 strategic trends will pave the way for an intelligent digital grid. All technologies cover advanced machine learning techniques and development artificial intelligence, the interpenetration of the physical and digital worlds.
1. Artificial intelligence and machine learning
In 2017, researchers will turn their attention to natural language processing and neural networks. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) will go beyond classical computing and begin to serve to create systems that can learn on their own. the world. That is, STS will help automate tasks and solve problems associated with the “information about everything” trend.
Advanced algorithms will make just “smart” cars intelligent – from unmanned vehicles to virtual assistants.
Gartner experts advise organizations to think about how they can use these technologies to be competitive.
2. Intelligent applications
These can be programs that help a person in everyday affairs, like a “smart” email sorter. Another option is more sophisticated virtual assistants, including business-oriented ones. Gartner experts say that by 2018, most of the world's largest companies will start using intelligent applications to improve the customer experience.
3. "Smart" things
This list includes already known devices, such as drones, unmanned vehicles or 3D printers. We are also talking about gadgets of the future, intelligently interacting with a person. The so-called "Internet of Things" (IoT: Internet of Things) will be created. These can be sensors in production, smart prostheses and chips in medicine, devices that ensure the safety of children, and much more.
4. Virtual (VR) and augmented (AR) reality
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are already widely used. VR works great in conveying the unique experience of other people and is used in distance learning. AR will allow various businesses to overlay graphics on objects in real time, of course, this will improve the production process.
Such technologies are becoming more and more accessible. You don't need to buy a $1,000 VR headset, but just $15 cardboard smartphone goggles. With their help, you can easily watch 3D videos and “walk around” in various places on our planet.
5. Digital twins
This is the name of a dynamic model of a physical thing or environment based on sensory sensors. This technology will be used in various fields for modeling, analysis and control. The digital twin, for example, in industry, will reveal weak spots real system for repair. According to experts, over the next 3-5 years, "hundreds of millions of things" will acquire digital twins.
6. Blockchain
In another way, blockchain technology is called a "chain of distributed data". It exists in the form of a database and contains information about all transactions carried out by system participants. Information is stored in the form of a "chain of blocks", each of which contains a certain number of transactions.
But the possibilities of blockchain are not limited to cryptocurrencies. The technology can optimize large registries of governments and corporations, structure a large amount of data, and ensure transparency of any actions.
Another technology can help small and large businesses: increase efficiency, reduce staff and reduce paperwork to a minimum.
7. Dialogue systems
Gartner experts believe that a dynamic network will be created between people, processes, services and things. And it will be able to support intelligent digital ecosystems. In essence, this is a new digital experience of people interacting with each other and devices. Soon search engines, online services and various programs will be able to receive and correctly process any voice commands.
8. Digital technology platforms
In the future, every company will work with a combination of five digital technology platforms: information systems, customer experience, analytics and forecasting, IoT, and business ecosystems. In particular, the creation of new platforms, services for IoT and interactive systems will become one of the key areas until 2020. So companies must decide how they will develop platforms to solve digital business problems.
9. Mechanics of applications and services
Technology is penetrating everywhere, human interaction with the digital world is already becoming a continuous process. This happens due to the global spread of the Internet, connecting all major devices to it and synchronizing them. The simplest example is a smart home.
Such interpenetration of technologies will allow us to optimally use all components of the global IT network (smartphone, laptop, car, TV).
10. Adaptive Security Architecture
With the increase in the number of hacker attacks, companies will have to think about digital security. Multi-layered security will soon become an important requirement for any enterprise. According to experts, IT leaders should focus on identifying and eliminating threats.
This is where blockchain technology can come in handy. The fact is that when using it, identification of a person, control and verification of reliability take minimal time. In addition, the blockchain guarantees absolute accuracy.
Technological innovations aimed at architects are beginning to develop and gain popularity.
Here is a list of 10 amazing architectural technologies of 2017 that show what our future will look like in a few years.
1. Roofs with integrated solar panels maximally adapted to the coatings familiar to our eyes. They will be assistants in solving the problem of climate change and making a positive impact on the environment.
2. Smart home technologies , from the Panasonic pot that stirs the sauce itself, to the Nest wireless thermostat that learns your behavior and adjusts the temperature of your home accordingly, or the Amazon Echo smart speaker that relays your voice commands to other appliances. A smart home, the latest technologies of which are striking in their diversity, is gradually becoming more accessible. Notable Companies constantly improving devices that allow you to connect existing and new gadgets into a single network.

3. generative design, that is, the creation of visual images with the help of a technique capable of not only “thinking”, but also determining the aesthetics of the product. This is a creative partnership between a person and a program that uses a certain algorithm in the processing of visual data.

4. Additive Design, i.e. 3D printing on an industrial scale. Various Chinese companies and United Arab Emirates regularly demonstrate how wide the possibilities of this technology are. Among especially interesting achievements- the development of Autodesk, which created software allowing to produce complex structures using the energy of conventional computing systems.
5. Mobile applications, which are good assistants to architects and offer useful developments for all stages of the project, from the creation of a concept to the actual construction.

6. Cloud service. BIM (Building Information Modeling) - building information modeling, i.e. the collection and processing of absolutely all information about the structure: architectural, design, technological, economic and any other. It turns out that with the help of BIM, an object is designed as a single architectural, technological, economic entity, and if you change the parameters in one area, they will automatically change in another.

7. A virtual reality. VR technologies are a world created by technical means, transmitted to a person through his senses: sight, hearing, smell, touch. Virtual reality simulates both exposure and responses to exposure. To create a convincing complex of sensations of reality, a computer synthesis of the properties and reactions of virtual reality is performed in real time.

8. Augmented reality. AR technologies are the result of introducing any sensory data into the field of perception in order to supplement information about the environment and improve the perception of information. For example, the Microsoft HoloLens mixed reality glasses allow building plans, marketing and other 2D materials to be superimposed on a 3D BIM model. With the development of mobile devices, augmented reality is becoming an integral part of workflows in architecture, construction and design.

9. Touch screen for CAD and BIM. Touch screens are used to view drawings on the go. This gadget will be the impetus for the development and improvement of touch screens aimed at architects and designers.

Last update: 12/27/2018
Artificial intelligence, voice control and virtual reality - this is the year when science fiction is slowly becoming reality. Have you heard such a law that it is human nature to overestimate the impact of technology in the short term and underestimate it in the long term? We will try to bring ready-made working things that will penetrate into our lives. New technologies in 2017 cover advanced machine learning and the development of artificial intelligence, the interpenetration of the physical and digital worlds.
The goal of many technologists is to easily implement in everyday life technical innovations that you never thought you would need, but now you can't live without them. Some products have almost reached the point of perfection. The mobile phone, for example, will be redesigned, but there are no significant improvements expected in the foreseeable future. So what's next?
The new wave of technological progress is so futuristic that it looks like a wild figurative fantasy. Expected this year are computers that can talk, robots that can learn, and virtual reality experiences that are incredibly immersive. Here MR PORTER predicts (very closely) the future and highlights the most important trends and Hi-tech that will literally change your world in the coming months.
Talking computer

Headphones for sound engineering your world

We've all heard of wearable technology and devices. A new product category in 2017 is "audible" technology, which will play music, transmit phone calls, monitor health indicators such as heart rate and blood pressure, and so on. These audible headphones from Doppler Labs in San Francisco are expected to launch in March for £250 called Here One. Basically, it's a pair of independent Bluetooth headphones. But it also lets you control the sound from the real world around you. So you can use them to tune the built-in microphones to the person sitting in front of you while turning down a crying baby across the restaurant; turn down the noise of an engine in flight, or the squeal of an underground train.
Fully immersive virtual reality
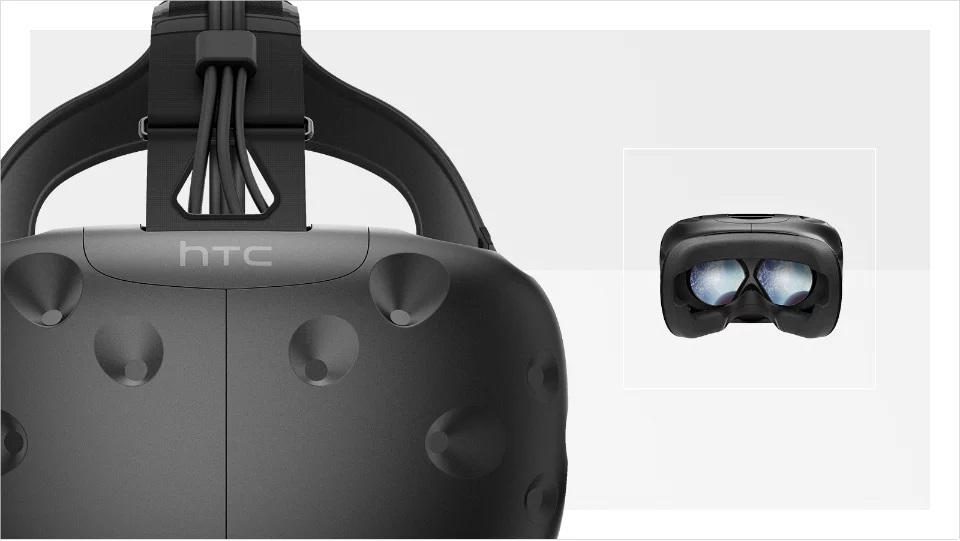

HTC Vive
Social media for adults
Vero
Social media applications are at the center of the over-sharing that is taking over the lives of teenagers - sometimes leaving their parents bewildered. But now there are social applications for adults. Vero is one of the most impressive and subtle inventions as it allows you to have more control over your news and choose who sees what. Thus, there is less danger in handing out too much information. You can discuss things like music, movies and restaurant recommendations with specific groups that might be really interested in them. Less social media, more social life.
smart robot
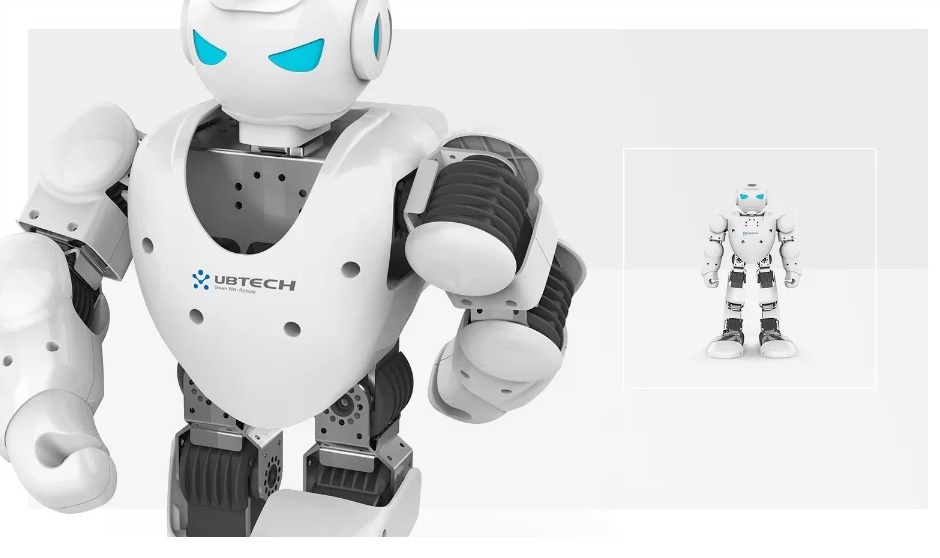

Ubtech Robotics Alpha 1S
One day robots will take over the world. For now, they're just taking over your living room. UBTech Robotics Alpha 1S until he brings you a cup of tea and does the laundry, but with 16 motors, his movements are quite realistic. It's a smart tech invention with some seriously impressive moves: this robot can breakdance, train, or just keep kids busy for hours. This all makes it worth £400. The little guy comes with software so you can teach him to do more tricks.
The suitcase that won't get lost

Raden A28 Check
The best technology is the one that solves the real problem. Losing luggage is a long-term concern for those who fly regularly. A28 Check from a New York startup Raden is a beautifully built suitcase that you can track with an app on your smartphone. So you will always know where he is, even when he is where he should be. It weighs itself, so you never have to suffer the shame of repacking at check-in to avoid unnecessary baggage fees. And it can charge your phone up to four times. The app will also help with other travel-related issues such as time-of-flight updates. The usefulness of the invention has been proven.
Aircraft with fixed wings
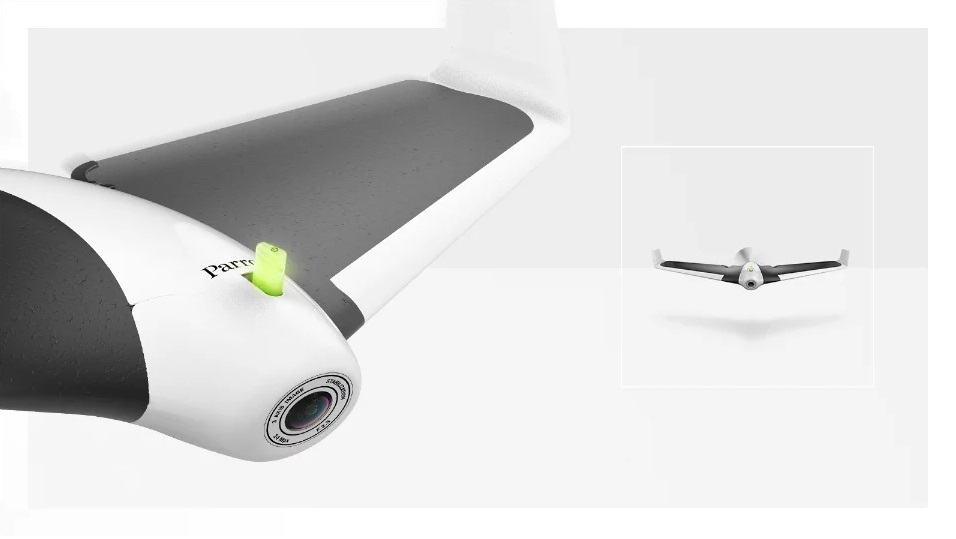

Parrot Disco FPV
Aircraft are increasingly being used for everything from filming to shooting in the treetops and, for the most part, they are all derivatives of the helicopter - helicopters with four, six or eight blades. With fixed wings, an unmanned aircraft looks more traditional. French company Parrot launched its first unmanned jet aircraft Disco for £1150. It is much faster than its bladed opponents, flying at speeds up to 50 miles per hour. It also comes with Parrot Cockpit Glasses, a headset that records HD video so you can effectively be a pilot on board and feel like you're flying. This is extraordinary technology for those who were brought up on model airplanes with rubber bands for the engine.
Update from 12/28/2017. And yet, from the height of the past year, we can conclude that there were no innovative technologies. There was a smooth improvement of existing machines and programs. Plus, the main focus was on personal items, one might even say entertainment and hedonism. All the same, they promise more large-scale changes. But in fact, it would be wrong to condemn the lack of innovation. Major innovations are always revolutionary and rarely happen. Therefore, it is better to be expressed in terms of innovation and improvement.
What if drinking water could be easily obtained from desert air without the use of electricity? What if a doctor could biopsy a suspected cancer patient without any kind of blade? The innovations that will make these and other predictions a reality are expected to become part of our lives very soon. Scientific Americanand Expert NetworkWorld Economic Forum talked about the 10 most advanced technologies of 2017 that can change the usual way of life. In the second part of the text, we will talk about five more of them. Read about the top five technologies.
ENGINEERING: Precision farming increases yields
As the global population grows, farmers will need to produce more and more food. However, arable land cannot expand, and a threatening food security threat can easily escalate into regional or even global instability. To adapt to new challenges, large farms are increasingly using precision farming to increase yields, reduce waste and mitigate economic risks.
Conventional farming relies on planting, harvesting, irrigation, and pesticide and fertilizer application decisions based on regional conditions and historical data. Precision or precision farming, on the other hand, uses sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data analysis software to ensure proper crop care without increasing the workforce. Stationary or robotic sensors and cameras seamlessly send images of individual plants and data about them to the computer - say, information about the size of the stem, the shape of the leaf and the moisture content of the soil around the plant. Farmers receive real-time feedback and then deliver water, pesticides or fertilizers in calibrated doses only to areas that need it. This technology can also help farmers decide when to grow and harvest.
As a result, precision farming can improve time management, reduce water and chemical consumption, and produce healthier, higher quality crops - all of which benefit farmers and conserve resources while reducing chemical runoff.

Many startups today are developing new software, sensors, antenna-based data, and other tools for precision farming. Large companies such as Monsanto, John Deere, Bayer, Dow and DuPont are doing the same. As part of these developments, seed producers are applying technologies to improve “plant phenotyping”. Over time, by analyzing individual plants (which ones thrive and under what conditions), companies can correlate plant responses to the environment with their genomics. This information, in turn, allows companies to produce seeds that will grow best in certain soils and weather conditions.
CARS: Hydrogen vehicles in the mass market
Battery-powered electric vehicles that don't emit carbon dioxide while driving will soon become mainstream transportation despite accounting for less than 1% of rolling stock on roads worldwide today. Numerous innovations in features such as cost and battery life have made prices so competitive that Tesla has more than 400,000 pre-orders for the $35,000 model, which is scheduled to go on sale in mid-2018.
Unfortunately, the other big hope for non-carbon vehicles - those that run on hydrogen-powered fuel cells - are too expensive to sell widely. However, many labs and businesses plan to cut costs by replacing one of the most expensive components in fuel cells, the catalyst. Many commercial fuel cell catalysts contain the precious metal platinum, which is not only expensive but also too rare to support widespread use in vehicles.

Researchers are trying to reduce the content of platinum in various ways: they suggest using it more efficiently by replacing the metal (in whole or in part) with palladium or any other inexpensive metal such as nickel, copper, and so on. Commercial catalysts typically consist of thin layers of platinum nanoparticles deposited on a carbon film, so researchers are also testing alternative substrates.
Stanislav S. Wong and his colleagues combine relatively small amounts of platinum or palladium with cheaper metals such as iron, nickel or copper, producing many alloyed grades that are much more active than commercial catalysts. Wong's group turned metals into ultrathin one-dimensional nanowires (about two nanometers in diameter). They have a high surface area to volume ratio, which increases the number of active sites for catalytic reactions.
Naturally, platinum-free catalysts would be ideal. At the end of 2016 sang hoon yu from the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in South Korea reported that the carbon nanotube catalyst doped with iron and nitrogen has an activity comparable to commercial catalysts. Besides, Liming Dai of Case Western Reserve University and colleagues have invented a catalyst that contains no metal at all - this is carbon foam doped with nitrogen and phosphorus, which is just as active as standard catalysts.
Finding and preparing a material that has excellent catalytic activity is only part of the challenge, Wong notes. Researchers are also working to expand existing laboratory manufacturing methods to ensure consistency in potency and longevity of the best options. Throughout the work, experimenters are assisted by theorists who apply complex computer models to figure out how all sorts of variables affect performance, from chemical compositions, sizes and shapes of metal nanoparticles, to detailed architectures of supporting structures. Such collaboration, Wong says, should one day enable the rational development of superior catalysts for affordable fuel cell vehicles.
MEDICINE AND BIOTECH: Genomic vaccines (composed of DNA and RNA instead of protein) fight infectious diseases
Standard vaccines for the prevention of infectious diseases consist of killed or attenuated pathogens or proteins from these microorganisms. Vaccines that treat cancer also depend on proteins. A promising new kind of vaccine is made up of genes. Genomic vaccines promise many benefits, including rapid production when a virus like Zika or Ebola suddenly becomes more virulent or common. Dozens of genomic vaccines have already entered the clinical trial phase.

Most vaccines work by teaching the immune system to recognize the enemy. Genomic vaccines take the form of DNA or RNA that codes for the desired proteins. When injected, the genes enter the cells, which then secrete the selected proteins. Compared to manufactured proteins in cells or eggs, obtaining genetic material should be easier and cheaper. In addition, one vaccine may include coding sequences for several proteins and can be easily modified.
A number of clinical trials are currently underway to test safety and immunogenicity, including for avian influenza, Ebola, hepatitis C, HIV, and breast, lung, prostate, pancreatic, and other cancers. One study is already showing effectiveness: The National Institutes of Health has launched a multidisciplinary clinical trial to test whether a DNA vaccine can protect against Zika.
ENERGY: Sustainable design drastically reduces waste
In the last decade, the construction and modernization of detached houses to reduce energy and water consumption has increased dramatically. However, applying green design to multiple buildings at once can be an even better idea. Sharing resources and infrastructure can reduce waste, and upgrading impoverished or moderate-income neighborhoods can also save people money.
One notable example is the Oakland EcoBlock project, which is led by the University of California, Berkeley. Harrison Fraker, Professor of Architecture and Urban Design. This is a multidisciplinary event that brings together urban designers, engineers, sociologists and policy experts from cities, states and federal governments, academia, the private sector, non-profit organizations and community organizations.

The program, which has been planned in great detail, will see the construction of 30 to 40 contiguous old homes in a low- and middle-income neighborhood near California's famous Golden Gate Bridge. The project aims to apply existing technologies to drastically reduce fossil fuel and water consumption, as well as greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers, while ensuring the long-term comfort and safety of residents, expect a quick recovery of funds spent on infrastructure.
The researchers plan to install solar panels on buildings throughout the community, sending energy to a smart microgrid (a local power system that involves the creation of its own power grid structures in a certain area that can operate autonomously). Excess solar energy will be stored. The community will also share electric vehicles that will have access to local charging stations. These measures should cut annual electricity consumption by more than half and bring carbon emissions to zero.
The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that up to 50% of California's water consumption is spent on lawns and gardens. The researchers estimate that the reorganization at the level of the EcoBlock system will reduce the demand for drinking water by up to 70%. Developers will treat and reuse wastewater from toilets, as well as water discharged from sewage and washing machines. The recycled liquid will be spent on gardening and irrigation. They will also collect rainwater and deliver it to toilets and washers, install efficient fixtures and faucets. The treated solid waste, meanwhile, will be incorporated into the compost.
COMPUTING: Quantum computing becomes more accessible and helps solve new problems
Quantum computing has captured the minds of mankind for almost 50 years. The reason is simple: they offer a way to solve problems that cannot be solved by classical machines. So, quantum computing can help solve the issue of chemistry simulation specifically for the development of new molecules and materials, solving complex optimization problems.
Until recently, only specialists in a few laboratories around the world had access to prototype quantum computers. But progress over the past few years has made it possible to build the world's first examples of such devices, which can finally test ideas, algorithms and other methods that have so far been strictly theoretical.

Existing machines are still too small to fully solve problems more complex than what supercomputers can handle today. However, the developers have made huge progress: algorithms have been created that will run faster on a quantum machine. Currently, there are methods that increase the coherence (lifetime of quantum information) in superconducting quantum bits by more than 100 times compared to a decade ago. In 2016, IBM made the first quantum computer publicly available in the cloud with a graphical interface for programming it, now based on the popular Python programming language. The opening of this system to the world stimulates innovation, which is vital to the achievement of this technology. To date, more than 20 published scientific papers use the quantum computing tool. Academic research groups, over 50 startups and major corporations around the world are focused on making quantum computing a reality.














