Eastern Slavs in the 8th and 9th centuries presentation. Presentation on history "Eastern Slavs in antiquity"
Unions of Slavic tribes and their settlement
- The chronicle “The Tale of Bygone Years” (Nestor) tells about the settlement of the East Slavic tribes.
- In the 6th-7th centuries, the Eastern Slavs formed tribal unions; historians count 15 of them.
- And after these brothers, their family began to reign near the glades, and the Drevlyans had their own reign, and the Dregovichi had theirs, and the Slavs had their own in Novgorod, and another on the Polota River, where the Polotsk people were. From these latter came the Krivichi, sitting in the upper reaches of the Volga, and in the upper reaches of the Dvina, and in the upper reaches of the Dnieper, their city is Smolensk; This is where the Krivichi sit. The northerners also come from them. And on Belozero he sits all over, and on Lake Rostov he meryas, and on Lake Kleshchina he also meryas. And along the Oka River - where it flows into the Volga - there are the Muroma, speaking their own language, and the Cheremis, speaking their own language, and the Mordovians, speaking their own language. Just who speaks Slavic in Rus': the Polyans, the Drevlyans, the Novgorodians, the Polochans, the Dregovichis, the Northerners, the Buzhanians, so called because they sat along the Bug, and then began to be called the Volynians.
- in the middle reaches of the Dnieper - glade,
- to the north of them are the northerners;
- in the Pripyat River basin - Dregovichi (from "dryagva" - swamp) and Drevlyans;
- on the Sozh River - Radimichi;
- in the Smolensk region and to the north - Krivichi;
- on Lake Ilmen and the Volkhov River - Ilmen Slovenes;
- in the northeast (area of Vladimir and Moscow) - Vyatichi;
- in the southwest (western Ukraine) - Ulichi, Tivertsy, Volynians.
- The main occupation is agriculture:
- slash-and-burn agriculture spread in the forest belt (northern regions),
- fallow (fallow) agriculture spread in the forest-steppe zone (southern regions),
- arable farming.
- The Slavs were engaged in:
- hunting,
- beekeeping (collecting honey from wild bees),
- craft,
- Important trade routes passed through the territory inhabited by the Eastern Slavs: “from the Varangians to the Greeks,” “from the Varangians to the Persians,” but the domestic market was poorly developed.
- Chronicle of PVL: “I live each with my clan and in my place, owning each of my clan.”
- V.O. Klyuchevsky: “The clan union rested on two pillars: on the power of the clan elder and the indivisibility of the clan property. The clan cult, the veneration of ancestors sanctified and strengthened both of these pillars.”
- A clan community is a group of blood relatives who have common property and run the household together.
- A neighborhood community is a more fragmented association based on the separation of individual small families from a clan.
- The neighboring community was called "mir" - in the south, and "rope" - in the north.
- East Slavic society was governed by the principle of military democracy. At the head of the tribe was a prince, supported by a squad (military nobility). The most important element of the structure of society was the veche.
- Prince
- military squad
- elders
- In the 8th-9th centuries, Slavic society was already approaching the emergence of statehood.
- military nobility
- Religion was an essential part of the life of the ancient Slavs. In the 7th-10th centuries, the Eastern Slavs were pagans and polytheists.
- Polytheism is polytheism, belief in many gods.
- Paganism - (from the Old Slavonic "pagans" - foreign peoples who did not accept Christianity) a worldview based on the worship of many gods, idolatry.
- Svarog
- Stribog
- Dazhdbog
- Veles
- Perun
- Makosh
- Yarila
- The pagan priests were the Magi. Sacrifices (demands) were made to the gods at certain places (temples), where images of the gods (idols) were placed.
- There was also an annual cycle of agricultural holidays, and fortune telling and omens were common.
To use presentation previews, create an account for yourself ( account) Google and log in: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
History of Russia, 10th grade. INDO-EUROPEANS. HISTORICAL ROOTS OF THE SLAVS. EASTERN SLAVS IN 8-9 CENTURIES.
Geographic Natural-climatic Ethnic Confessional subjective FACTORS AFFECTING THE DEVELOPMENT OF RUSSIA: HISTORICAL SOURCES: - Substantial - LINGUISTIC - ETHNOGRAPHIC - WRITTEN
Years of life Origin Education Achievements Personal life HISTORIAN SCIENTISTS STUDYING THE HISTORY OF RUSSIA: N.M.KARAMZIN (1766-1826) N.I.KOSTOMAROV (1817-1885) S.M.SOLOVIEV (1820-1879) V.O.KLUCHEVSKY (1841-19110 S.F.PLATONOV (1860-1933) S.B.VESELOVSKY (1876-1952) A.V.ARTSIKHOVSKY (1902-1978) D.S.LIKHACHEV (1906-1999) A.P.OKLADNIKOV ( 1920-1980) B.A.RYBAKOV (1908-1998) A.A.ZIMIN (1920-1980) V.L.YANIN (1929-) A.N.SAKHAROV (1930-)
INDO-EUROPEANS ARE AN ANCIENT POPULATION OF EUROPE AND ASIA, WHO GAVE THE BEGINNING TO MODERN EUROPEAN AND ASIAN PEOPLES, AND LATER, SPREADED IN NORTH AND SOUTH AMERICA, AUSTRALIA, NEW ZEALAND.
TRIBES INFLUENCED THE SETTLEMENT OF THE SLAVS: Germans (2 thousand BC) Cimmerians Scythians (6-4 centuries BC) Sarmatians (2 centuries BC) Huns (5-6 centuries BC) c.) ANTY - a powerful alliance of Slavic tribes in the basins of the Dnieper and Dniester rivers, 5th century. “..they cannot stand slavery; brave and courageous; hardy and hardworking; kind to strangers; excellent warriors..."
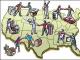
Polyana Novgorod Slovenes Dregovichi Drevlyans Vyatichi Krivichi Polotsk Northerners Radimichi Volynians Buzhans Ulichi Tivertsy Croats Dulebs TRIBAL UNIONS OF SLAVS (15):
From the shores of the Baltic - European coast - to the Mediterranean Sea - Rome - Constantinople - north along the Black Sea coast - north along the Dnieper - portage to the Lovat river - Lake Ilmen - Volkhov river - Lake Ladoga - Neva river - across Gulf of Finland to the Baltic Sea. TRADE ROUTE “FROM VARYAGS TO GREEKS”
Prince Voivode Druzhinniki (squad) Youths (junior squad = personal guard of the prince) Tribal nobility Veche Smerda Husbands Warriors In the family: husband/servants/servants Poor peasants Slaves SOCIAL ORDER
HOMEWORK: 1) PARAGRAPH 1, READ, PAY ATTENTION TO THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ANTS (P.18-20) AND THE LEGEND ABOUT THE BOOK. KIE (P.20-22) 2) PARAGRAPH 2, UNDERSTAND BY QUESTIONS: Q.1, Q.2 (KNOW TRIBAL UNIONS, TRACE ON THE MAP ON P.27), Q.5 (ANALYSIS OF THE SOCIAL SYSTEM); PART OF THE PARAGRAPH ON P.34-37 UNDERSTAND “PECULIARITIES OF RELIGION AND RITES OF THE SLAVS” INDEPENDENTLY
On the topic: methodological developments, presentations and notes
The emergence of a state among the Eastern Slavs.
Lesson on forming new knowledge with elements role playing game. An advanced task is given to 6 students who will act as historians. During the lesson the following concepts are practiced: state, Varangian (norm...
Kuban studies lesson "Life and culture of the Circassians and Cossacks", "Social performances of the Circassians and Cossacks", "Paganism - the ancient religion of the Eastern Slavs"
I offer a lesson in 6th grade "Paganism - ancient religion Eastern Slavs" presented in the form of a presentation. The lesson gives brief information about the most revered pagan deities. Lessons in 7th grade on...
lessons of Kuban studies "Life and culture of the Circassians and Cossacks", "Social speeches of the Circassians and Cossacks", "Paganism - the ancient religion of the Eastern Slavs"
I offer a lesson for 6th grade “Paganism - the ancient religion of the Eastern Slavs” presented in the form of a presentation. The lesson provides brief information about the most revered pagan deities. Lessons in 7th grade on...
In today's lesson you will get acquainted with the ancient Slavic tribes, the peculiarities of their economy and life, and learn the names of the gods worshiped by the Eastern Slavs and their neighbors.
Topic: Old Russian state
Lesson:East Slavs VVII - IXcenturies
In the 7th - 9th centuries. the Slavs occupied a vast territory of Eastern Europe. They settled in the territory from Lake Ladoga to the middle reaches of the Dnieper River, from the Bug River to the upper reaches of the Dnieper. A feature of the settlement of the Slavs was that the tribal unions of the Eastern Slavs formed in the basins large rivers, where centers of tribal principalities subsequently arose. The Ilmen Slavs settled in the area of Lake Ilmen and the Dvina River. The Dregovichi and Drevlyans settled in the area of the Pripyat River. In the upper reaches of the Dnieper along the Sozh and Seim rivers lived the Radimichi. In the middle reaches of the Dnieper, glades settled. In the Desna River basin there are northerners. In the northeast, in the Oka River basin, there are Vyatichi.
Rice. 1. Settlement of the Eastern Slavs ()
The main occupations of the Slavs were based on the characteristics of the land. Slash-and-burn agriculture was practiced in the forests. The steppe land was developed through fallow land. But still the yield was low due to the harsh continental climate. Other industries of the Slavs were fishing, hunting, and beekeeping was also common. The Novgorod-Ilmen region was rich in forests, and the fur trade flourished there. IN southern regions Hunting for moose and bears was practiced. The abundance of rivers, lakes, and a well-branched water transport system contributed to the development of shipping, trade, and various crafts that provided products for exchange. Large cities and tribal centers such as Kyiv and others were founded at the crossroads of trade routes.

Rice. 2. Slash-and-burn farming ()
On the eve of the formation of statehood, the Eastern Slavs lived as a neighboring community, in which private property took shape. Each family had the right to cleared land - lyadina. In Slavic society, military leaders were identified and a squad was formed. The squad is special group population engaged only military activities, in particular hiking. For defense, there was a militia of free community members. The warriors not only participated in campaigns of conquest, but also ruled the annexed lands. At its head was a prince, to whom the squad and governors were subordinate. Lower in position were smerds or, as they were also called, husbands (heads of patriarchal families who had the right to participate in the army). The servants had an even lower status - these were members of the husbands' families and slaves who did not have the right to participate in the army.
The religion of the Eastern Slavs was complex, varied, with detailed customs. Its origins go back to Indo-European ancient beliefs, to Paleolithic times. The religion that existed among different peoples before they adopted Christianity or Islam was called paganism (polytheism). The Slavs populated the world with different gods and goddesses. At their head was the great Svarog, the god of the universe. His sons - Svarozhichi - the sun and fire, were carriers of light and warmth. The sun god Dazhdbog was highly revered by the Slavs. The Slavs prayed to the clan and women in labor - the god and goddesses of fertility. This cult was associated with the agricultural activities of the population and therefore was especially popular. God Veles was revered by the Slavs as the patron of cattle breeding, Stribog commanded the winds. As the Slavs merged with some Iranian and Finno-Ugric tribes, their gods migrated to the Slavic pantheon. Thus, in the 8th - 9th centuries, the Slavs revered the Iranian sun god Khoros. With the beginning of military campaigns among the Slavs, the god of thunder and lightning, Perun, borrowed from the Balts, increasingly came to the fore. Appears special treatment to fallen soldiers (funeral pyres, burial mounds, etc.). The Slavs had an annual cycle of agricultural holidays: Kolyada, the day of the vernal equinox, Maslenitsa, May 1-2 celebrated the appearance of the first spring shoots, the holiday of Ivan Kupala, and so on. Many of these holidays have survived to this day. In every house the Slavs had idols of gods; there was also a cult of Shurov, small family idols of houses.

The Slavs did not have friendly relations with all their neighbors. Slavic legends tell about the attack of the Turkic-speaking nomads Avars on the Slavic tribe of Dulebs. In the 8th century, the East Slavic tribes of the Polans, Severians, Vyatichi and Radimichi conquered the Khazars, forcing them to pay tribute.
So, living surrounded by various tribes and peoples, the Eastern Slavs formed a special civilization.
- Mavrodin V.V. Where did the Russian land come from? M., 1986.
- Rybakov B.A. World of history. The initial centuries of Russian history. M., 1984
- WWW.GRANDARS.RU ().
- Academician ().
- TAREFER.RU ().
- When did the Slavs appear on the territory of our country?
- How did nature influence the activities and beliefs of the Eastern Slavs?
- What were the relationships between the Slavs and neighboring tribes and peoples?
MKOU Secondary School No. 2 Stavropol Territory, Kochubeevsky District. History and Social Studies Teacher Fedorova Valentina Petrovna .

Eastern Slavs in antiquity 8-9 centuries.
- 1. Settlement of the Eastern Slavs.
- 2. Economy of the Eastern Slavs
- 3. Prerequisites for the formation of the Old Russian state
- 4. Social system of the Slavs.
- 5. The reign of Igor.
- 6. Basic theories of the formation of the ancient Russian state.
- 7. Board Olga (lessons and churchyards)

Eastern Slavs in the 8th and 9th centuries
“The Tale of Bygone Years” is the oldest work on Russian history. This is a whole encyclopedia of the life of our state from the 9th to the 11th centuries. From it we learn about the events that took place in those distant times, and about language, and about the origin of writing, about geographical knowledge and art, about international relations. Previously it was believed that the author of this chronicle is the monk of the Kiev Pechersk Monastery, Nestor, who lived at the turn of the 11th-12th centuries. But research has shown that one person could not be the author of the entire work. It was developed by several generations of chroniclers, who added new things to the story of their predecessor. The chronicle was found by chance by Musin-Pushkin. If from Kievan Rus Since nothing has reached us except “The Tale of Bygone Years,” then this work alone would be enough to imagine the height of Russian culture of that time.

East Slavic tribes in the 8th-9th centuries.
In the 8th century, the land where the Indo-Europeans lived, and later the Balto-Slavs, was inhabited by a Slavic population who spoke the Slavic language, and large tribal unions were formed from related tribes. At that time there were about 15 of them. Their names corresponded to the territory: polyana (fields); Drevlyans (forests); Dryagovichi (quagmire).
Between the Slavs and the surrounding
there were clashes between tribes,
but basically the relationship was good neighborly. The Slavs did not impose
others have their own customs and traditions.

Economy of the Eastern Slavs
1. Agriculture- first - slash-and-burn, fallow, and then - arable: two-field and three-field (rawl with a runner, millstones for grinding, manure the earth, there was an agricultural calendar);
2. Cattle breeding(goats, sheep, cows and poultry). Draft force - horse and ox; horse breeding for combatants;
3. Fishing, where there is an abundance of rivers and lakes;
4. beekeeping- collecting honey and wax, which was highly valued;
5. Hunting(wolves, foxes, beavers, bears, martens). Hence the first monetary unit - kuna (marten) .

Prerequisites for the formation of a state
Russian word“state” comes from the word “gospodar”, sovereign (“master”, “lord”. This word was originally associated with the power of the leader. The tribal prince became such a ruler among the East Slavic tribes . The state meant the emergence of a central government, uniting the entire territory in which this or that people lives, united by force or good will. During the time of Kiya there were the first signs
government structure

Prerequisites for the formation of the state
1. Thanks to the progress of the economy, an individual family could feed itself;
2. Family property was divided into separate family property;
3. The right of private ownership, private property arose;
4.Under these conditions, the power and economic capabilities of tribal leaders and elders sharply increased.
5. Families left without the support of the tribal community were helped by the authorities of the nascent state.

Social structure of the Eastern Slavs in the 8th-9th centuries.
By the end of the 9th century, a hierarchy had developed (multi-level)
People are stinkers-free, wealthy- husbands ;
Voi those who could equip themselves and take part in the war;
Servants-family members who were subordinate to their husbands;
Orphans, slaves, wretched, meager, beggars - disadvantaged, poor, dependent on the rich;
Slaves- the lowest on the social level. Mostly prisoners, but this category has not taken root with us for a number of reasons.
Squad (boyars, youths)
Princes of tribal unions
The Grand Duke was traditionally considered the supreme ruler and owner of the land in Rus'. But his power was not sole, it was limited boyars and veche. Because he was chosen by the tribal assembly.

The religion of the Eastern Slavs is paganism (polytheism, polytheism).
Nature, great and unknowable, gentle and unpredictable, was the main deity of the Slavs. With the advent of the princes Perun .
ghoul-evil spirit beregin good
goblin, rus a lka,
brownie - too much
bride kidnapping
Magi, magicians -
favorites of the gods.
At the head- Svarog- god of the Universe;
Son of Svarog Dazhdbog(sun god) Slavs - Dazhd's grandchildren;
Rhoda- goddess of fertility;
Veles the cattle god;
Stribo Mr. lord of the winds;
Makosh- patroness of the female part of the household.

Basic theories of education Old Russian state
Norman (Bayer, Schlozer, Miller)
Anti-Normanskaya (M. Lomonosov)
Founders Old Russian state- Normans, whom the Slavs called to their lands to rule them;
Among the Eastern Slavs there was a process of decomposition of the tribal system and the development of feudalism, the formation of statehood before the arrival of the Varangians.
Title "Rus" Scandinavian origin.
Title "Rus" is of Slavic origin.
Slavs not capable to create their own statehood.
“The Russians, Slovenians, Krivichi and everyone said: “Our land is great and abundant, but there is no order in it. Come reign and rule over us."
There is no evidence of the existence of the name "Rus" in Scandinavia.
Influence Scandinavians for education slightly .

The beginning of the Rurik dynasty.
There are two centers in Rus': Novgorod (Oleg-Igor) in the north, and Kiev (Askold and Dir) in the south. Oleg took possession of Smolensk, Lyubich, and then Kiev . In 882 - unification of lands - the beginning of the Russian state .
862 g. Three brothers arrived from the Varangian lands to the Slavic and Finno-Ugric lands with their families: Rurik(first ruled in Ladoga, and then in Novgorod), Sineus(in Beloozero) and Truvor(Izborsk).
Rurik united the north and north-west of the East Slavic and Finno-Ugric tribes.
879 Rurik died
Remained son - Igor
Everything is in your hands
Oleg. Who is he?
Appeared
dynasty
Rurikovich ruled until 1598

Foreign policy Oleg.
He sought to seize the mouths of the Dnieper and Danube, to establish himself in the Northern Black Sea region and the Balkans, and to control the Kerch Straits.
1. Campaigns against the Drevlyans, northerners, Radimichi - imposed tribute on them
2. According to the peace treaty of 898, Rus' paid tribute to the Hungarians (200 l) after the defeat.
3.907 and 911 campaign against Byzantium (Oleg’s cunning) - the first written agreement in the history of Eastern Europe. Not only trade union, but also military.
“Your shield is on the gates of Constantinople.”

Reign of Igor (912-945)
Duchess Olga. Who is she? The daughter of a ferryman or a noble family?
1.941 g. campaign against the Greeks. We saw Greek fire for the first time. The campaign ended in defeat.
2.944 g. campaign against the Greeks - the Greeks paid off with tribute.
3.945 g a trip to the Slavic tribes of Polyudye (the local residents accumulated everything they were rich in)
945 g. the murder of Igor by the Drevlyans (“If a wolf gets into the habit of the sheep, he carries out the whole herd until they kill him,” so said Prince Maly).

Reign of Princess Olga.
955 - baptism of Princess Olga in Constantinople. Godfather Tsar Constantine.
1.B 945 took revenge on the Drevlyans for the death of her husband, Igor.
2. Established lessons and churchyards - the end of the people. I installed the cart. This means princely power...
3. Sent an embassy to Germany to Emperor Otto 1 to establish friendly relations and strengthening religious ties. The pagans refused to be baptized. Some of the bishop's people were killed. Olga was canonized .
Eastern Slavs in the 8th-9th centuries. 1.East Slavic tribes in the 8th-9th centuries. 2. Economy of the Eastern Slavs 3. Prerequisites for the formation of the state 4. Social system of the Eastern Slavs 5. The path “from the Varangians to the Greeks” 6. Religion of the Eastern Slavs 7. Rituals and legends 8. Magi and magicians
1. East Slavic tribes in the 8th-9th centuries. During the 8th century. in the territories where first the Indo-European, later the Balto-Slavic, and then the Slavic population lived, large tribes were being formed. By that time there were about 15 of them. In the Middle Dnieper region, a union of glades (dwellers of the fields) had formed. Kyiv became their center.









The glades had an agricultural calendar. They bred: cattle, sheep, goats, geese, chickens... Oxen were the draft force, but horses were increasingly used. Fishing was a secondary trade. They were engaged in hunting ( valuable fur went for exchange and sale; was a means of payment) Coins in Rus' were called kuns (martens)


3. Prerequisites for the formation of the state The Russian word “state” comes from the words “gospodar”, “sovereign”, “master”. The state meant the emergence of a central power uniting the entire territory in which the people live. The state is the power of the prince and his associates. This is the army, laws, taxes Religion was part of the state system


Stormy social processes took place near the glades and Novgorod Slovenians: -The tribal community disintegrated -The family led by a man became the center of social life -The tribal property was divided into separate land holdings-The right of private ownership, private property was born -A neighboring community appeared -The power of tribal leaders and elders increased -Chiefs undertook long and short campaigns -Conquered tribes were subject to tribute

4 Social system of the Eastern Slavs By the end of the 9th century. a clear hierarchy of society had developed: -At its top was the prince, in whose hands all management was concentrated -He relied on warriors loyal to him -Next to the prince stood out the governor - the leader of the tribal army -The prince's personal guard - youths (younger warriors)