Bulbous flower home hippeastrum. Hippeastrum care at home, transplantation and propagation
Blooming hippeastrum fascinates with its beauty. Only once a year he pleases us with huge star flowers. And what a disappointment it can be when the long-awaited flower does not appear, or the plant begins to fade altogether. To avoid such troubles and be able to enjoy the contemplation of this miracle flower, you need to know some secrets of care and stick to them. The grateful plant will certainly please the eye with generous flowering.
Description of hippeastrum
Appearance
Hippeastrum (lat. Hippeastrum) is a perennial bulbous plant. The leaves are linear, shiny leaves, 50–70 cm long, 4–5 cm wide, and have shallow grooves on the surface. The leaves are arranged in two rows. During the flowering period, the plant produces a powerful, tall (up to 60–80 cm) peduncle.
The name of the flower is translated from ancient Greek as “star horseman”.
Hippeastrum during flowering is a source of pride and admiration
The flowers are funnel-shaped. Their color range is quite wide: red, white, orange, pink, purple, sometimes yellow or greenish shades. The main tone can be supplemented with strokes or specks.
The flowers are large - up to 20 cm in diameter, collected in an umbrella inflorescence. Hippeastrum has a very faint odor. Some species have no smell at all. This is a great advantage for people prone to allergic reactions.
Hippeastrum flowering - video
Natural habitat and home maintenance
The homeland of hippeastrum is the American tropics and subtropics, in particular the Amazon basin. It was brought to Europe in the 16th century and quickly gained admirers around the world. In 1799, the first hybrid Hippeastrum Johnson was bred. Today these flowers are widely used as a houseplant and are also grown for cutting. Hippeastrums are not particularly difficult to care for. Even novice gardeners can easily cope with this task.
Variety of hippeastrum varieties
This plant belongs to the Amaryllis family and has about 90 species and more than 2 thousand varieties.
IN indoor floriculture The most commonly cultivated plant is hippeastrum hybrida. The classification of varietal hippeastrums is based on two characteristics: flower size and shape. Depending on this, plants are conventionally divided into 9 groups, which are indicated in the table.
The most popular groups and varieties of hippeastrum - table
| Group name | Popular varieties |
| Large-flowered simple | Apple Blossom, Charisma, Showmaster, Minerva, Hermes |
| Medium flowered simple | Lemon Star, Magic Green |
| Small-flowered simple | Santa Cruz, Giraffe, Baby Star, Bianca, Neon |
| Terry large-flowered | Blossom Peacock, White Peacock, Sweet Nymphs, Dance Queen, Aphrodite, Lady Jane |
| Terry medium-flowered | Alfresco, Uniquay, Double Record, Elvas, Pasadena, |
| Terry small-flowered | Zombie |
| Sibistr | La Paz, Emerald, Chico, Rio Negro, Tiramisu, Melfi |
| Orchids | Papilio, Exotic Star, Ruby Star |
| Tubular | Pink Floyd, Amputo, Santiago, Germa, Rebecca |
Magnificent hippeastrums in the photo
 Simple large-flowered hippeastrum with rim
Simple large-flowered hippeastrum with rim  Simple large-flowered hippeastrum striped
Simple large-flowered hippeastrum striped  Simple medium-flowered hippeastrum
Simple medium-flowered hippeastrum  Simple medium-flowered hippeastrum with figured edge
Simple medium-flowered hippeastrum with figured edge 
 Simple small-flowered hippeastrum
Simple small-flowered hippeastrum  "Star" splendor
"Star" splendor  Charming bouquet
Charming bouquet 
 Double-flowered hippeastrum
Double-flowered hippeastrum  Double large-flowered hippeastrum
Double large-flowered hippeastrum  Sibistr
Sibistr  Orchid hippeastrum
Orchid hippeastrum  Orchid Hippeastrum
Orchid Hippeastrum
Similarities and differences with amaryllis
Amaryllis is often classified as a hippeastrum variety, but this is erroneous.
Drainage is a prerequisite for prevention excess moisture soil and rotting of the bulb and roots
The bulb is planted in a slightly moist soil mixture, deepening it to a maximum of 2/3 of the height.
A narrow pot and shallow planting help create optimal conditions for hippeastrum
After planting, the plant only needs warmth. There is no need to water the hippeastrum until sprouts appear.
If any damage is noticed on the bulb, it must first be healed. This procedure includes trimming the rotten parts, soaking for 30 minutes in a fungicide solution (Fundazol, Maxim) or ordinary brilliant green and drying for 24 hours.
Such a bulb must be planted in soil where humus is replaced with a small amount of sphagnum (peat moss).
It is advisable to bury the reanimated bulb into the soil to no more than 1/4 of its height. With such planting, it is easier to control its condition and, if necessary, carry out spraying. After the bulb has recovered, it is easy to add soil mixture to the usual level.
Having planted the plant in moist soil, place it in a warm, slightly shaded place (you can cover it with an empty pot) and exclude watering until the peduncle is forced to a height of 10 cm.
The optimal frequency of hippeastrum transplantation is once every 3–4 years. A favorable time is the threshold of the rest period or its end. It is advisable to use the transshipment method when replanting - moving the plant along with the earthen lump. In this case, there is minimal damage root system, which contributes to the rapid rooting of the bulb and its active development.
Transshipment method - a method of transplantation with minimal damage to the root system
Basic rules for caring for hippeastrum
Watering and fertilizing
As discussed above, the intensity of watering of hippeastrum is directly related to its life cycle. However, it is important to provide the plant not only with the required amount of moisture, but also to correctly deliver it to the root system.
For example, it is not recommended to pour water on the onion - it may rot. It is better to combine top watering with tray watering. This way the moisture will be evenly distributed throughout the earthen ball, which will prevent rotting of the roots. The main rule for watering hippeastrum: it is better to underwater than to overwater. You also need to regularly wipe the leaves from dust or wash them with warm water.
During the growth of the peduncle, when it reaches a height of 12–15 cm, it is useful to water the soil with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. 5-6 days after this, you need to feed the plant with phosphorus fertilizer.
Hippeastrum is fertilized regularly, at the beginning of the growing season - once every two weeks with liquid nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium (7:3:6) fertilizer (for deciduous plants). After the leaves appear, to stimulate the active formation of buds, hippeastrum requires less nitrogen and much more potassium, so the ratio of mineral components changes to 4:6:12 (for flowering plants). The frequency of feeding is maintained.
A month before the onset of the dormant period, hippeastrum needs fertilizers with a small amount of nitrogen and phosphorus and a large amount of potassium (4: 4: 12).
Carefully read the directions for applying fertilizers on the packaging and do not exceed the specified concentration of minerals. Otherwise, you can burn the root system of the plant.
Timely balanced feeding promotes high-quality flowering and growth of foliage mass. The bases of the leaves form the scales of the bulb and it increases in size. In case of insufficient nutrition or complete absence of fertilizing, the bulb will use nutrients, accumulated from leaves, but they are not enough to ensure flowering.
Some secrets of flowering
Sometimes hippeastrum disappoints gardeners by refusing to bloom. Why? There may be several reasons:
- Most often, the plant does not throw out a peduncle due to exhaustion of the bulb. Hippeastrum requires a significant amount of nutrients for flowering. It is not surprising that the soil in the pot quickly becomes depleted. To avoid such problems, it is necessary to fertilize regularly and in sufficient quantities.
- A plant affected by pests (spider mites, scale insects or scale insects) tries to fight them and does not have the strength to flower.
- Hippeastrum does not bloom even when the bulb rots, which occurs due to waterlogging of the soil.
To admire the blooming hippeastrum year after year, you should not allow such situations. It is also useful to know some tricks of experienced gardeners to ensure 100% flowering of this plant:
- treating the bulb before planting with hot (43–45 ºC) water for three hours will cause the plant to bloom in three weeks;
- if you stop watering in August, move the plant to a dark, dry place and keep it there until the end of January, and then resume watering, the flowers will delight you in 1.5 months;
- If you cut off all the leaves in July and do not water the hippeastrum for a month, and introduce a liquid complex fertilizer with the first watering, the flowers will bloom in August or September.
To avoid burning the roots, fertilizer should be applied only after preliminary moistening of the soil.
Immediately after flowering, it is necessary to cut off the withered peduncle, continuing to water and fertilize. And prepare the plant for proper rest (rest period). The next flowering directly depends on this.
Rest period
The natural dormant period of the hippeastrum lasts quite a long time: from September to January. If your plant grew outdoors in the summer, by the beginning of autumn you need to bring it into the house and gradually reduce watering until the leaves stop completely and dry out. You can independently trim the yellowed leaves from which the bulb has already taken nutrients.
The quality of the next flowering depends on the dormant period
After this, you should place (or place the pot with the plant on its side) in a dark and cool (5–12 ° C) room. Many gardeners keep them at more high temperature- about 17–18 °C. The soil must be lightly moistened once every 2–3 weeks to prevent the roots from drying out. It is not recommended to wet or spray the bulb.
The dormant period should last 1.5–3 months, depending on the planned time of subsequent flowering of the plant. During this time, the hippeastrum does not “show signs of life.” The development of leaves and peduncles occurs only inside the bulb.
After the rest period, it is time for the hippeastrum to wake up. Leaves and flower stalks appear on the surface of the bulb.
Simultaneous appearance of leaves and peduncle
Problems waking up after wintering
If the bulb does not wake up, you can, of course, be patient and wait for it to awaken on its own. But, as a rule, a “late” bulb will not produce full flowering.
In this case, it is worth remembering in what state the plant “retired”. After all, the peduncle is formed in the axil of every fourth leaf. If last year the green mass was not sufficiently expanded, the bulb will be weakened.
And if there were fewer than four leaves, then the hippeastrum will probably refuse to bloom in the new season. Dry content can hardly help here. It is necessary to provide a very warm temperature, actively water and feed.
Care errors and their correction
Caring for hippeastrum is not very difficult, but it is necessary to follow the rules of watering, fertilizing and lighting at different periods of the plant’s life cycle.
Common mistakes in caring for hippeastrum - table
| Care errors | Their manifestation | Fixes |
| No rest period (air temperature above 18°C, regular watering and/or fertilizing) | Lack of flower bud formation and, as a result, flowering. | Follow the described rules of watering and fertilizing, maintain temperature regime, corresponding to each stage of the plant life cycle. |
| Low air temperature (below 17°C) during flowering | ||
| Poor lighting during active growth | ||
| Violation of the rules of watering and fertilizing (lack of it) | ||
| Overwatering | Abrupt cessation of growth, rotting of the bulb, development of pests in the soil. | Dig it up, free it from the soil, remove damaged parts of the plant if necessary, and replant it in clean soil. |
| Keeping at low temperature or damp | Darkening or blackening of flowers. | Cut off damaged flowers, move the plant to a warm, dry place and maintain optimal growing conditions. |
| Insufficient feeding with potassium fertilizers or keeping them in too dry a room during the growing season | Browning of leaf tips. | Feed with mineral fertilizer containing macro- and microelements and fertilize in accordance with the phase of plant development, humidify the air. |
| Lighting too bright | Fading flowers. | Provide diffuse lighting, avoiding direct sunlight. |
Diseases and pests of hippeastrum
Hippeastrum is not too susceptible to disease. It is most often affected by red burn (red burn fungus or stagonosporosis), red rot and false powdery mildew. Some pests can also bother this plant: spider mites, scale insects, aphids, and scale insects. You can determine what ails a plant by its appearance.
The main diseases and pests of hippeastrum and methods of combating them - table
| Diseases and pests | Causes | External signsplant damage | Consequences | Prevention and treatment measures |
| Red burn (red burn fungus or stagonospora) | Fungal infectious disease. Ripe spores are carried by the wind, infecting healthy plants. | Red oblong spots on all parts of the plant. | Severe damage leads to curvature and wilting of leaves and peduncles, disease of daughter bulbs | For minor damage, it is enough to spray the affected areas with fungicides. The effect of this procedure lasts up to a month. The most effective products contain copper: copper sulfate, Hom, AbigaPik, Celeste Topa suspension concentrate. You can also use drugs such as Maxim and Rovral, Skor, Vitaros, Previkur, Ordan, Fundazol, Topaz. Bulbs with significant damage should be dug up and all diseased areas should be removed, including the roots and peduncle (in a flowering plant). Only immediate treatment gives a positive result. Do not leave a sick plant for a period of rest. Several effective ways to process bulbs:
After processing, the bulbs should be dried for at least two days. Plant them in clean soil and ensure daily loosening of the soil until new roots form. |
| Viral disease. | Silvery spots on leaves. | Soft leaves, weak, short peduncles or lack thereof. | Treat the leaves with a fungicide. | |
| Excessive waterlogging | Limp hanging leaves, rot on bulb scales and roots (on the upper scales it may look like red spots, like a red burn). | Withering of leaves, absence of flower stalks, and with severe damage - rotting of the root system and death of the plant. |
|
|
| Infection from other plants or through open windows, purchase of an infected bulb. | A white cotton-like coating secreted by mobile insects measuring 0.5–1.2 mm. | They significantly slow down the development of plants by sucking the juice out of them. |
|
|
| Shchitovka | A small and dangerous pest of indoor plants with a hard shell surface that secretes honeydew (sticky liquid). | Creates a favorable environment for the development of various fungal diseases. Plants stop growing and drop leaves and flowers. |
||
| Aphid | Dense clusters of sedentary green, gray or orange insects measuring 1–5 mm on young shoots. | Sucks the juice out of the plant. Buds, flowers and leaves lose color and fall off. |
||
| Cobwebs on the underside of leaves, woven by an almost invisible mite, 0.1–0.3 mm in size. | The leaves and peduncle become covered with “marble” spots, become fragile, twist, turn yellow and fall off. |
The most common diseases and pests of hippeastrum in the photo
 A bulb affected by a red burn
A bulb affected by a red burn  Leaves affected by stagonosporosis
Leaves affected by stagonosporosis  Partial damage to the bulb by red rot
Partial damage to the bulb by red rot  The root system is almost completely destroyed by red rot
The root system is almost completely destroyed by red rot  Leaves and peduncle affected by downy mildew
Leaves and peduncle affected by downy mildew  Abundant spread of mealybug on leaves
Abundant spread of mealybug on leaves 
Reproduction
Hippeastrums reproduce in two ways: seed and vegetative.
Seed method
The seed method is quite complex and time-consuming. Seeds are formed only 1.5–2 months after flowering. But they do not form on their own. It is necessary to artificially pollinate the pistils and stamens. The grown ovary has the appearance of a large tricuspid box.
Ripening of hippeastrum seeds
Inside the box there are rows of flattened seeds of irregular round shape. They are characterized by a black color with a brown tint and the presence of thin black wings.
Seeds ready for sowing
In spring they are planted in sandy-leaf soil. It is important to consider that freshly harvested seeds have 100% germination. As a rule, only 30% of the total amount of dried seeds germinates. The shoots will delight you in 15–5 days.
Sprouted hippeastrum seeds
When the leaves grow to 6–10 cm, they are transplanted into pots with a diameter of 6–7 cm. At this time, the bulb grows.
Grown-up hippeastrum seedlings
The period before the first flowering of young plants of different varieties ranges from two to five years. This method is more acceptable for breeders. Most amateur gardeners consider it costly and ineffective. However, there is no guarantee that the maternal characteristics of the plant will be preserved.
Vegetative method
It is much easier to propagate hippeastrum vegetatively. Several variations of it are practiced.
Reproduction by daughter bulbs
This is natural, and therefore the most optimal and simplest way. Three-year-old bulbs proper care Usually they give 3 children.
Bulb separation
They are separated with a sterile sharp instrument, treating the cuts with crushed coal. Planted in accordance with the rules for planting an adult bulb.
For two years, the newly planted plant is not deprived of foliage and is not put to rest. The growth of the bulb and the formation of a peduncle in it depends on the intensity of leaf growth. With good care, the children will throw out flower stalks in 2-3 years.
Dividing the bulb
Split onion
Division is carried out during the maximum accumulation of nutrients in the bulb - in November.
Division process algorithm:
- Remove the top layer of soil, leaving only the bottom of the bulb in the soil.
- Remove external dry scales.
- Cut off the leaves along with the top of the bulb.
- Cut the onion into four equal parts to the surface of the soil.
- Insert knitting needles with a diameter of 5–6 cm into the cuts to prevent the parts of the bulb from closing.
- Follow all the rules for caring for an adult plant.
- When the leaves appear, fertilize and continue fertilizing according to the standard scheme.
- Next spring, divide the bulb and plant the parts in separate flowerpots.
You can divide the onion in another way: cut it, leaving a piece of bottom and scales in each part. It is useful to sprinkle the sections with charcoal or activated carbon. Plant the resulting slices in a light peat mixture.
surface planting in light substrate
After 40–50 days, babies appear and need to be planted in pots in the spring.
Attention! When planting, we must not forget about the presence of toxic substances in hippeastrum bulbs and adhere to safety rules.
In the Amaryllidaceae family, the genus Hippeastrum alone has about 90 species. The most popular flower is valued by gardeners for its stunningly beautiful and high-rising inflorescence. However, it is difficult to achieve such a result, because the tropical lord of the flora world is finicky and requires special treatment. Let's figure out together how to properly care for hippeastrums so that they reciprocate.
Types and classification
Landing
If you bought an already blooming hippeastrum, then you need to prepare a new pot, fill in the drainage, add the required amount of soil (a universal mixture for ornamental house plants), and transfer the plant there from the container for sale. Make sure that the roots are not damaged.
Hippeastrum bulbs are acquired in the autumn-winter period, when the plant is dormant. Before planting in the ground in spring, the bulb must be soaked in warm water for 2-3 hours (this is how the plant is forced). Then it should be planted so that almost half of the bulb is above the ground.

Hippeastrum (hypeastrum, Hippeastrum, cont. hyperastrum, hipperastrum), which is often not quite correctly called amaryllis (amaryllis)– spectacular indoor flower, which usually appears in our homes during the Winter holidays. Huge bright flowers hippeastrum on thick stems and several basal linear leaves grow from a large bulb. What to do with hippeastrum after flowering? Why doesn't indoor hippeastrum bloom? Read about caring for hippeastrum in a pot, growing, replanting and propagating this beautiful indoor plant.
Hippeastrum or amaryllis?
Hippeastrum comes from South America, belongs to the family amaryllis and looks very similar to another famous plant: amaryllis belladonna ( Amaryllis belladonna) from South Africa, which we talked about in the article. Name confusion plants goes back very deeply, to the brilliant Carl Linnaeus, who back in the 18th century unmistakably identified the family plants and appropriated hippeastrum funny name amaryllis horseman, horse amaryllis (Amaryllis equestris), presumably, having seen in beautiful flower resemblance to a horse's head. In the 19th century, another prominent botanist D.W. Herbert upon closer examination amaryllis equestrian noticed that the resemblance to Amaryllis belladonna rather superficial, and separated the first into a separate genus, reflecting the connection with the horseman in the Greek name: hippeastrum, or star riders . Although hippeastrum belongs to its own genus, many people call the plant in the old way: amaryllis , or amaryllis - hippeastrum .
Hippeastrum: flowering
So, you have a blooming one at home hippeastrum in a pot. Care It is very simple to look after a plant that is gaining buds or is already flowering. Hold hippeastrum in a bright place at room temperature (not higher than 20°C), away from a heating source, turning over occasionally pot different sides to the light. This is necessary so that long peduncles with hippeastrum flowers grew straight. When turning the plant over, be careful: hippeastrum in a pot easily loses balance due to heavy and long peduncles. Water regularly hippeastrum, avoiding stagnation of water in the pots.
With the beginning hippeastrum flowering move the pot to a cooler place (15–18°C). Lower temperatures will extend the period hippeastrum flowering.
Hippeastrum: care after flowering
After the hippeastrum blooms cut off the wilted flower and wait for the peduncle to die naturally. Now you can carefully pull it out of the bulb. Hippeastrum care at this stage consists of regular watering, keeping them in bright light and feeding with a weak solution of fertilizer for flowering plants indoor plants(you can use a weak fertilizer solution for, or). All these conditions are important for hippeastrum flowering next winter, because the germ of a new flower is laid in hippeastrum bulb in this period. Lack of bright lighting and good care after hippeastrum flowering and in summer - the answer to a frequently asked question, why does hippeastrum not bloom? next season.
When warm weather sets in, you can take out hippeastrum on a bright balcony, loggia, in an unheated greenhouse or in a garden. Water all summer hippeastrum abundantly and regularly, protect the plant from direct sunlight and fertilize weekly. If hippeastrum spends the summer in the garden, make sure that they cannot reach him. By the end of summer - beginning of autumn hippeastrum leaves may begin to turn yellow.
Hippeastrum: preparation for new flowering, forcing bulbs, timing
To hippeastrum bloomed by the end of December, by, at the end of summer, the conditions of detention are changed plants. Hippeastrum in a pot move to a cool place (10-13°C) - on a terrace, garage, greenhouse or left in the garden. Lighting doesn't matter at this stage forcing of hippeastrum. Watering hippeastrum, as well as fertilizing, stop completely so that the soil is in potty dried up and hippeastrum leaves withered and died naturally. This forcing stage can last from 4 to 12 weeks. Bulbs during the dormant period (when the leaves have wilted) can be stored in the refrigerator, in the vegetable compartment, wrapped in paper. During storage, care must be taken to hippeastrum bulbs Do not get any moisture, otherwise they may rot.

At the second stage of distillation bulbs, hippeastrum transfer to a warm, dark room (some recommend the top shelf in the boiler room) and water generously once so that the soil is completely soaked. Now the hippeastrum is left for a week or two until it produces a peduncle with buds. The soil is not allowed to dry out completely, keeping it slightly moist. When the peduncle appears, the hippeastrum is placed on a sunny windowsill and regular watering is resumed, avoiding stagnation of water in the pots.
Hippeastrum flowering occurs 4-6 weeks from the start of the second stage forcing. Knowing the date you need and by which you want to receive blooming hippeastrum, count down to calculate the exact start time of the second stage of forcing.
Hippeastrum: planting and transplanting bulbs, propagation

Indoor hippeastrum in a pot A transplant is needed every few years. Hippeastrum transplantation done during the rest period bulbs, before the start of the second stage of forcing. During transplantation, they also Hippeastrum reproduction baby (small bulbs with roots growing from an adult bulb). Such plants They will bloom in 3-4 years. Small during transplantation hippeastrum bulbs can be carefully separated from the mother, trying to preserve as many roots as possible. Children are planted in small pots (see below) and cared for exactly like adult plants, with the exception of forcing, which is not done in the first years. Little ones hippeastrum bulbs It will also require replanting into larger pots as it grows. When grown up hippeastrum bulbs reach a diameter of 7 cm, they will begin to bloom.
Purchased from a garden center hippeastrum bulbs Can plant at any time in autumn and winter, following the rules of the second stage of forcing (they have already undergone the first stage of forcing in the nursery). Before planting roots in the ground hippeastrum soak for several hours in water at room temperature. Adults hippeastrum bulbs from the store will bloom 4-6 weeks after planting. Having planted several hippeastrum bulbs at different times, you can get continuous flowering of these beautiful plants from late November until late spring.
Plant and replant hippeastrum bulbs in small pots. Size hippeastrum pot should only be one and a half centimeters larger than the size bulbs along the radius of the pot. Use a good quality potting mix for indoor plants, mixed with coconut fiber or perlite (for better water permeability) in a ratio of 3:1. When planting, sprinkle with soil and compact hippeastrum bulb only 2/3: the upper part of the bulb remains open above the soil surface.
Related Articles

At the end of winter, lilies bloom on the windowsills of many apartments. This is the colloquial name for hippeastrum of the amaryllis family. Large flowers of different shades, collected in inflorescences, delight the eye on the eve of spring and give a good mood. This article contains useful tips care indoor hippeastrum at home.
In nature, the “cavalier star”, as hippeastrum is translated, grows in the tropical part of the American continent. It is found on mountain slopes and plateaus of Venezuela, Mexico, and Brazil. In the eighteenth century, sailors and traders began to bring exotic plants to Europe from their trips overseas and care for them. Botanists began researching and describing unknown plants. At the same time, the construction of greenhouses began, which appeared in botanical gardens and private estates.

Hippeastrum in natural conditions
At this time, botanists discovered and described several species of lilies, which were called amaryllis. At the beginning of the 19th century, a new genus was identified - hippeastrum. It also includes some types of amaryllis. This led to many hippeastrum being called amaryllis. This misconception still persists among amateur gardeners.
And only in 1954, at a congress of botanists around the world, it was confirmed that there is only one species belonging to the amaryllis family, called Amaryllis beautiful. At the same time, there are about eighty species of hippeastrum belonging to the same family.
Appearance
Hybrid hippeastrum, grown at home, has long, wide leaves, reaching seven centimeters in width and more than half a meter in length. The plant's bulb is large, up to ten centimeters in diameter. The peduncle often exceeds one meter. There are large flowers on it, the diameter of which reaches twenty centimeters. The number of flowers on a peduncle can vary from two to ten. Hippeastrum flowers come in a variety of colors and shades - from dark red to white. Colors with dots, spots of a different color, with a transition of shades from the funnel to the edge of the flower are common.
Differences between Hippeastrum and Amaryllis
People often confuse amaryllis and hippeastrum, because the plants look very similar and belong to the same family. But they have significant differences, which are shown in the table.
| Amaryllis | Hippeastrum | |
| Homeland | South Africa | Tropics of America |
| Bulb shape | Pear-shaped, with gray scales | Round or elongated, with brown-yellow scales |
| Number of flowers in inflorescence | From 6 to 12 | From 2 to 6, less often up to 9-10 |
| Flowering time | Autumn | End of winter - beginning of spring |
| Peduncle | Without cavity | Hollow inside |
| Leaves | Narrow, grooved, smooth | Depending on the type, they can be smooth or rough, elongated |
Hippeastrum became widespread as indoor plant thanks to its unpretentiousness. It is enough to comply simple rules care during the period of dormancy and flowering, and it will delight you with its flowers. The big advantage of hippeastrum is the possibility of forcing, which allows you to achieve flowering by a certain date.
Varieties of indoor Hippeastrum
The abundance of “cavalier star” species required their classification. IN different countries highlight their own color groups. Basically, varieties of hippeastrum are divided into simple and double, orchid-like, with long-tubular flowers and miniature hybrids.
Let's look at the most popular indoor varieties.

Lady Jane
Variety Lady Jane has large double flowers of a peach hue with pink veins in the center of the petals. The diameter of the flowers reaches twenty centimeters.

Hippeastrum Leopolda
Hippeastrum Leopolda often found in home collections. Pink petals end with a white border. Inside a flower White color gradually acquires a pale green tint.

Hippeastrum spotted
Hippeastrum spotted- a low plant that throws out leaves after flowers appear. The petals are cream-colored and decorated with red dots, and the throat is yellowish-green.

Royal (Regina)
In the variety Royal (Regina) a flower of a rich red hue appears on a peduncle about half a meter high. Leaves appear after flowering. The number of colors ranges from two to four.

Narrow-leaved
Variety Narrow-leaved It is distinguished by narrow, slightly curved orange petals. The number of buds on one peduncle can reach nine.

parrot
TO rare species applies Hippeastrum Parrot-like. Its wide petals of a light green hue are decorated with longitudinal cherry-colored stripes. The peduncle, 90 cm high, is crowned with two to four buds.

Reticulate
Hippeastrum reticularis refers to low-growing varieties. Its peduncle does not grow higher than half a meter, and up to five buds of bright pink color with darker veins appear on it, forming a mesh pattern on the petals.
Landing

Pay attention to the red dots
Before planting the bulb, you need to pay attention to its condition. A healthy bulb should not have a red border and/or red dots, which indicate the presence of a fungal disease. If the bulb is purchased, then it should have dry brownish scales with living roots. If there are dents or grooves on it, then it is better to refuse such a purchase.
The pot for planting is selected so that there is a finger gap between the bulb and the wall, but no more than three centimeters. It is necessary to take into account that the plant grows tall, so the pot must be stable and deep enough.
How to plant hippeastrum? Drainage up to two centimeters thick is poured onto the bottom. For drainage, you can use expanded clay, small pieces of shards, and bricks. Then follows a layer of soil, which is poured into a mound. You can add a handful of sand under the roots of the bulb. Having placed the bulb on a mound, straighten the roots and carefully sprinkle with soil. The ground level should not be higher than the middle of the bulb.
Important! After planting, watering is carried out in the tray or along the edge of the pot, avoiding water getting on the bulb.
Hippeastrum is not picky about soil. To ensure lush flowering, it is recommended to prepare the soil yourself from the following components, which are taken in a 2:1:1:1 ratio:
- turf land;
- humus;
- peat;
- river sand.
A small amount of wood ash and bone meal are added to the mixture. If there is no flour, add superphosphate at the rate of two teaspoons per liter of soil. Phosphorus is necessary for the plant to bloom lushly. You can buy a ready-made earthen mixture for bulbous plants.
Important! If, after planting a new bulb, no leaves appear after a month and a half, then it is not viable.
Transfer
Hippeastrum is transplanted annually for young plants, then every other year. And old plants are replanted once every two to three years. But if the plant is not replanted, then the top layer of soil must be replaced annually.
When to replant hippeastrum? Traditionally, transplantation is carried out in the spring, after flowering has ended. But you can also replant in the fall, before the start of the dormant period. In the fall, plants that were planted (taken out) into the garden for the summer are replanted.
Before planting in a new pot, the bulb must be carefully examined for wounds and rot. It is better to throw away diseased bulbs. The onion is placed in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for half an hour. Long roots are trimmed, the cut areas and wounds are sprinkled with crushed activated carbon. The planting process and selection of land is described above.
Watering and fertilizing
Proper watering for hippeastrum is of great importance and depends on the period of plant development.
In September, before the start of the dormant period, watering is reduced. By the end of September, watering can be stopped completely if the flower is in a cool place. If you had to leave it in a warm room, you can slightly moisten the soil. During this period, the plant lives off the nutrients accumulated in the bulb.
After the end of the dormant period and the appearance of a peduncle, the plant is transferred to a warm, bright place. As the peduncle grows, watering is increased. From the beginning of flowering until the onset of the dormant period, the flower needs regular watering, avoiding water getting on the bulb. It is better to pour water into the pan.
Hippeastrum is fertilized with mineral fertilizers. It is advisable to use two types of fertilizers. In the spring, at the beginning of the growing season, fertilizing is applied to deciduous plants. Fertilizer for flowering plants is applied from the moment the buds appear until the end of flowering. The second stage of fertilizing for flowering plants begins from the end of leaf growth until the onset of the dormant period. The frequency of fertilizer application is from two to four times a month.
The plant does not require spraying. You can periodically wipe the leaves from dust with a damp sponge.
Where to put the pot

Hippeastrum loves sunlight
The plant loves sunlight, so it does well on windows facing south, southeast and southwest. In summer, on the south side it must be shaded from scorching rays. After flowering, leaves grow, nutrients accumulate in the bulb, and scales form.
The plant develops well at temperatures from 17 to 23 degrees Celsius, but higher temperatures do not harm it. During the dormant period, it is recommended to keep the flower in a cool, shaded place with a temperature of 10-15 degrees. If it is not possible to place the flower in a cool place, then you can leave it in the room, providing rare and weak soil moisture.
Rest period
Hippeastrum has a dormant period at the end of September - beginning of October. Most species have leaves that die and must then be removed. Some gardeners create an artificial dormant period for the flower, the duration of which should be one and a half to two months. Thus, you can achieve flowering by a certain date or two or three times a year.
It is possible to breed hippeastrum without a pronounced dormant period. It is kept in a regular sunny place with watering as the soil dries. With this regime, the plant can delight you with flowering in spring or autumn.
Hippeastrum flowering
With proper care and a dormant period, hippeastrum blooms in late winter - early spring. In mature plants, flowering is possible one more time - in summer. The number of peduncles depends on the care summer period and the number of sheets formed. The plant has a peculiarity: flower stalks are formed through four leaves. Therefore, than large quantity leaves will grow before the dormant period, the more flower stalks will appear on your plant. It is desirable that the number of leaves be at least seven or eight.

Hippeastrum blooms in late winter or early spring
If the bulb was purchased in winter and you want to quickly admire the flowering, it is recommended to keep it in warm water (forty degrees) for a couple of hours before planting. After planting, carefully water the soil and place in a warm, bright place. The next watering is carried out after the peduncle has grown ten centimeters.
After flowering ends, the peduncle must be trimmed, the plant is regularly watered and fed.
Why doesn't Hippeastrum bloom?
If the hippeastrum does not bloom, this means that the conditions of detention were violated:
- in spring and summer the plant did not receive the necessary minerals;
- lack of light during the growing season;
- the plant was at a low temperature.
Reproduction of Hippeastrum
Hippeastrum can be propagated in several ways.
Children's department
The easiest way is to separate the children. When transplanting, carefully separate the bulbs, the diameter of which should be at least two centimeters. The bulbs with roots are immersed in the ground two centimeters. The new plant will begin to bloom in three to four years.
Bulb division
 Unfortunately, not all types of hippeastrum produce babies. In addition, if the maintenance regime is violated, baby bulbs may not appear. Therefore, if it is necessary to propagate a flower, the method of dividing the bulbs is used.
Unfortunately, not all types of hippeastrum produce babies. In addition, if the maintenance regime is violated, baby bulbs may not appear. Therefore, if it is necessary to propagate a flower, the method of dividing the bulbs is used.
The leaves of the bulb are trimmed, the roots are trimmed to two centimeters. The bulb is cut into 2-4 parts so that the bottom with roots remains on each part, otherwise it will not take root. The cutting areas are sprinkled with activated carbon and left to dry for two to three days. When planting, only the lower part is deepened into the soil. The planting mixture is prepared from peat and sand in equal proportions. You can cut the onion into four parts, but not all the way. To dry the incisions, sticks are inserted into them. The cut onion is planted, covering only the lower uncut part with soil. It is recommended to water the separated bulbs from a tray. After some time, each slice gives birth to a baby. Propagation by dividing the bulb is recommended to be carried out in late autumn, while the bulb has a maximum supply of nutrients. The process of dividing the bulb is clearly shown in the video.
Reproduction by scales
The third method of division is called scale reproduction. With this method, the onion is cut into pieces (8-16) so that part of the bottom remains on each piece. The knife is disinfected with alcohol before cutting the onion. The cut slices are sprinkled with Kornevin and planted in sand or sphagnum moss. In this case, the tops should be outside. Containers for germination are placed in a warm place (at least 20 degrees).

Onion slices are planted in sand or sphagnum
Propagation by seeds
You can get new plants from seeds. To do this, you need to pollinate the flower and wait for the seeds to ripen. This will take up to two months. Seeds must be sown immediately after collection into the ground to a depth of one centimeter. After two to three weeks, sprouts appear. Containers with plants are placed in a bright place, shaded from the sun. This method of propagation is used by breeders to develop new varieties, because the bulb loses many useful substances.
Video: Hippeastrum from seeds at home.
Diseases and pests
Hippeastrum is a disease-resistant plant. Most often he suffers from a “red burn”. This name hides the insidious fungal disease stagonosporosis. Its signs can appear both on the leaves and on the bulb. Oblong red spots appear on the leaves. Red spots can also be found on the bulbs. The bulb becomes covered with wounds, softens and the plant may die. One of the signs of the disease is a stop in the growth and addition of leaves.

Red burn on leaves

Red burn on the bulb
When buying a bulb, you need to carefully examine it so that there are no red spots. The husk should be shiny and brownish in color. The head itself is solid, without any dents. If signs of disease appear at home, it is necessary to remove the bulb and inspect it. If there are small spots, they are cut out, and the wounds are treated with brilliant green or copper oxychloride. After drying for a week, the bulb is planted in fresh soil, pre-treated with a fungicide. The bulb is planted so that the bottom and roots are covered with soil. If the bulb is severely damaged and softened, it must be destroyed.
To prevent damage by Fusarium, the bulb is soaked for a couple of hours in a solution of potassium permanganate before planting. The disease manifests itself as yellowing of the leaves and drying out of the plant. The bulb is treated with brilliant green, and the soil is watered with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Among the pests, hippeastrum can be affected by spider mites, thrips and narcissus flies. The appearance of thrips is indicated by white spots and stripes on the outside of the leaves. The insects themselves can be found on the underside of the leaves. It is necessary to carry out two or three treatments with Actellik, Fitoverm or a similar drug with an interval of five days.
The daffodil fly lays eggs in the neck of a flower. The larvae penetrate deep into the bulb and damage it. The plant stops growing and blooming. It is recommended to check the bulb and treat it with Aktara. If the damage is severe, you have to get rid of the diseased plant.
Problems during cultivation
- With insufficient watering, the leaves turn pale and the flowers droop their heads. During flowering, it is necessary to keep the soil slightly moist.
- At low temperatures, the flowers begin to turn black. It is necessary to move the plant to a warm place.
- If the leaves turn pale and wither, this indicates excess moisture in the pot. It is necessary to reduce watering, after drying the soil.
- If the flowers become faded, then you need to shade them from the sun's rays.
- Hippeastrum leaves turn yellow and dry out on the eve of the dormant period. If this happens at another time, then pay attention to the violation in care (damp or cold). Check the plant for pests that can cause yellowing of the leaves.
With proper care and compliance with the watering and fertilizing regime, hippeastrum will delight you with its flowering every year.
The indoor flower hippeastrum is very popular. It pleases its owners with its attractive appearance, it is especially beautiful during flowering - once a year beautiful star flowers appear on it. The culture requires special care and maintenance, especially during the flowering period.
Botanical description
Hippeastrum (lat. Hippeástrum) is a type of bulbous crop of the Amaryllis family. Belongs to perennials. IN wildlife grows in South America, native to Mexico, Brazil. Found in alpine meadows and mountain slopes. It was brought to Europe in the 16th century, and appeared in Russia only in the middle of the 19th century.
In regions with mild climates, hippeastrum is grown in open ground and in room conditions. The flower bulb is round, cone-shaped, 5-10 cm in size. At its base there is a bunch-like root system, which is formed along the edge of the bottom. The roots are fleshy, soft, slightly branched. The foliage of the crop is linear, keeled on the lower side with a characteristic vein, and grooved on the upper side.
As the flower matures, there is an alternation of leaves with a closed base and with an open base. An inflorescence is formed in the axil of the latter. The part of the stem on which the 4th leaves and peduncle have formed represents a cycle.

During the growing season, two or three such periods are observed. After the appearance of the peduncle, it takes an average of 1-1.5 years before it begins to bloom. The peduncle is a thin cylindrical stem, reaching a height of 30-80 cm. It is colored light or dark green, depending on the species. The surface is sliding, slightly covered with a waxy coating.
The inflorescences are umbrella-shaped. Flowers are up to 15 cm long and up to 25 cm in diameter. The color differs depending on the variety of hippeastrum. Most often, flowers are presented in white, pink and red shades. Has 6 stamens. The fruit of the crop is a dry capsule. About 60-100 pieces of dark flat seeds are formed in it.
Types and varieties
The culture is often confused and mistakenly called amaryllis. In old sources you can find that two different plants are called the same. In the mid-50s of the XX century. International Congress it was decided to include only the species A. belladonna in the genus Amaryllis.
It is easy to distinguish amaryllis from hippeastrum. The first species has 6-12 inflorescences and an incomplete peduncle, and the second has 6-7 inflorescences and a full peduncle.

Modern garden hippeastrums are very diverse. Today you can find varieties with double and striped flowers. In total, about 600 hybrids of the crop are known. More often in indoor floriculture, G. hybrida (also known as h. Hybrida) is used. The plant is classified according to the size and shape of the flower.
In the catalog of hippeastrum varieties you can find:
- Large-flowered. Represented by the following varieties: Hermes, Apple Bloss, Charisma, Minerva.
- Medium flowered. The most popular varieties: Magic Green, Lemo nStar.
- Small-flowered. Representatives are: Neon, Santa Cruz, Giraffe.
- Terry large-flowered. The most common varieties are Blossom Peacock, White Peacock, Aphrodite, Lady Jane.
- Medium-flowered double. The group is represented by Alfresco, Double Record, and Pasadena varieties.
- Small-flowered double. The most striking representative is the Zombie variety; Sibistr. Representatives are La Paz, Esmeralda, Tiramisu, Rio Negro, Melfi.
- Orchids. Common varieties are Papilio, Ruby Star, Exotic Star;
- Tubular. Represented by the following varieties: Santiago, Pink Floyd, Rebecca.
Some varieties of hippeastrum in the photo:

Aphrodite



Santiago

Magic Green

Terry






Growing and care
When growing hippeastrum at home, special attention should be paid to caring for hippeastrum after flowering.
The following conditions are required:
- Watering– moderate. Before the next moistening, the soil should be slightly dry. Bottom and top watering is practiced. During the flowering period it is abundant. After the arrow forms (4-5 cm), watering increases. Do not allow water to come into contact with the bulb.
- Lighting– prefers bright and sunny places, but with diffused light.
- Trimming. After the end of the flowering period, the peduncle is cut off. At the same time, fertilizing and watering are not stopped - these activities are stopped only after a month.
- Place. Windows of any orientation are suitable. If the bulbs need to be grown, then preference is given to windows facing south, west or east.
- Temperature. Suitable temperature is 18-24°C. A regime below 5°C adversely affects flower development.
- Top dressing. Organic and mineral fertilizers are used for feeding. They are applied 2 times a month, alternating with each other. The optimal time for fertilizing is May-August.
- Keeping in open ground. Caring for hippeastrum in open ground is the same as when keeping it at home. In some cases, watering becomes more intense.
- Child care. During the flowering period, the flowering crop is protected from direct sunlight. If growth and development slows down, then the plant is moved to a warm place.
- Does not require irrigation. The leaves are regularly wiped clean from dust.
Secrets of caring for hippeastrum on video:
State of rest
For further successful flowering, the crop requires a state of dormancy. From the end of summer/beginning of autumn, preparations are gradually carried out. First, reduce watering and finish feeding. In November, soil moisture stops completely.
With decreasing period natural light and lack of watering, the leaves fall off at the beginning of winter. The plant's dormant state lasts from September to January. After completion, the bulb is transplanted to a new location. Next, the pot is placed on the windowsill.
Required conditions for keeping at rest: suitable temperature – 12-15°C. The bulb can tolerate a short drop in temperature to -1°C, watering is kept dry, no moisture is required. Lighting – complete absence of light.
Important! You should not cut off the foliage during the period of natural wilting - there is a reserve in it for subsequent development and flowering. Remaining useful material go into the bulb.
Hippeastrum flowering
As a rule, the flowering of hippeastrum begins in February-March. Some varieties bloom in late spring and summer.
You can achieve flowering yourself using forcing:
- Method 1. Place the onion in a container with water (40-45°C) for 2 hours. Flowering in many specimens begins on average after 3-4 weeks.
- Method 2. Watering is stopped at the end of August, after which the flower is placed in a dark place. In mid-January, watering resumes. Flowering of the Dutch hippeastrum after forcing begins after 1.5 months.
- Method 3. Watering is stopped at the end of July and the leaves are cut off. After a month, moisture is resumed, and fertilizer is applied at the same time. With this method, flowering begins in August-September.
Replanting an indoor lily
The indoor lily quickly absorbs all nutrients. For this reason, it is recommended to replant established plants every 2 years. It is preferable to carry out the event before dormancy or shortly before leaving dormancy. Approximate time August/January. Transplantation can be carried out at another period, having previously decided on the timing of flowering. It occurs approximately 1-2 months after planting.
Before transplanting the plant, the soil mixture is first prepared. You can use universal soil. Required condition– good soil drainage. Next, the bulb is buried in the ground two-thirds of its height. Moisturizing begins with the appearance of flower stalks.
Special attention is paid to the pot for the plant. It is preferable to use narrow and tall containers, because... The root system of the flower goes down. The distance between the walls of the pot and the bulb should not exceed 3-4 cm.
Practicing for the summer landing hippeastrum in open ground on the site. Pronounced benefits - the plant increases growth, the bulb becomes larger. But there is one drawback - the flower is more exposed to the risk of pest damage.
Reproduction methods
The culture is propagated by children, seeds and division of bulbs. The last method is the most effective - it allows you to preserve all varietal characteristics. The simplest of all, but not always possible, is reproduction by children. In some cases, a daughter bulb does not form from the mother bulb.
Seed method
At home, hippeastrum is often grown from seeds. They are prepared independently by first pollinating the flower. Ripening takes place within 2 months. The capsule is cut off, then the seed material is taken out. After this, the land is prepared and sowed.
It is important not to delay this process, as the seeds quickly lose their viability. Cover the container with glass and wait for the first shoots. They usually appear within 2-3 weeks. To accelerate the growth of young bulbs, a weak solution of mineral fertilizers is applied. From time to time the container is ventilated and watered.
Bulb division
How to propagate by dividing the bulbs: for this method, large bulbs of a brownish-golden color with smooth scales are selected. Cut them lengthwise into 4-6 pieces. Each of them should have part of the bottom and leaf scales located inside the bulb. Part of the foliage that is in the embryonic state is removed.
The separated and prepared parts are cut and treated with dry coal. Next, it is buried in the sand. It is kept moist at all times.
After about a month, picking is carried out - during this period, small roots and two full leaves should form. Afterwards, transplantation is carried out to a permanent place in the ground. Flowering of seedlings with proper care is observed after 3-5 years.
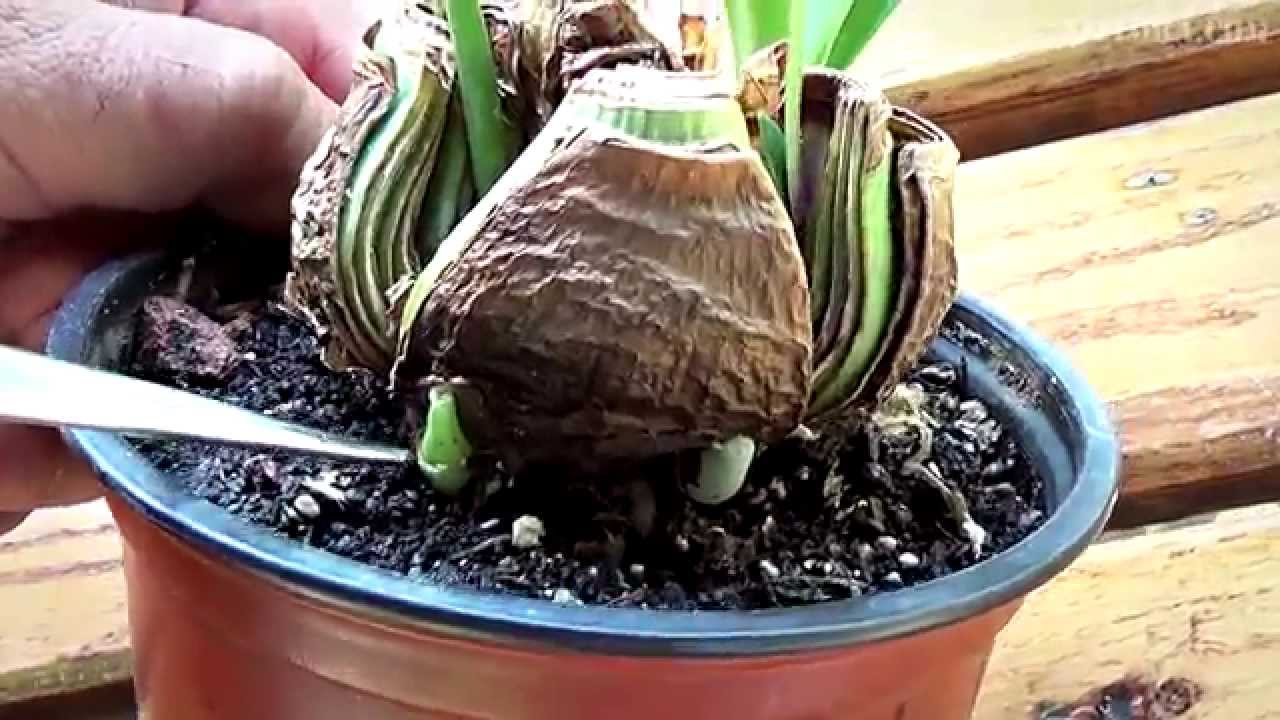

Reproduction by children
The method of propagation conveys all the characteristics of the mother flower. First, the daughter onions are separated from the main one. They are then buried in wet sand. Picking is carried out when the young plant has formed two small leaves. After 8-12 months, the flower is transplanted into deeper pots.
Caring for children - regular watering is provided and fertilizing is carried out. Flowering can be expected within 2-3 years.
Diseases and pests
Hippeastrum, both when kept at home and when grown in open ground, is susceptible to diseases. Besides characteristic features, there is a cessation of crop growth.
Spider mites and scale insects are pests that attack the plant. They are located under the scales of the bulbs and on the foliage. First, insects are removed using a rag soaked in an alcohol solution. Only then do they begin processing. Suitable products are a solution of karbofos or Actellik. If necessary, the plant is transplanted into a container with other soil.
Red rot of bulbs is a dangerous disease for crops. If the appearance of the hippeastrum deteriorates or growth stops, it is necessary to dig up the flower and inspect the underground part. If foci of infection are detected, damaged parts and dead roots are removed.
- treatment with Fundazol and dusting with ash;
- after processing for a week, the bulb is dried;
- the soil mixture is watered with a special solution for disinfection (Fludioxonil is suitable);
- then transplant into new land and watch the plant.
Mosaic virus is another disease of hippeastrum. When infected, yellowish spots appear on the leaves. The plant itself does not bloom and grows poorly.
A decrease in decorativeness or its complete loss is associated with improper maintenance conditions. If there is excessive dampness/low temperature, the flowers may darken. What to do - move the pot to a dry and warm place. Slight browning of the tips of the foliage may indicate a lack of potassium. In these cases, it is necessary to apply mineral fertilizers.
Exposition
Several blooming hippeastrums in the apartment are a unique sight. You can plant bulbs of different varieties in one pot, for example, Grand Diva, Sommertime, Rubistar. In some cases, flowers appear earlier than leaves; other crops with green foliage are planted next to them. The pot is selected in accordance with the design of the room.
As a rule, the forcing of hippeastrum is carried out for some holiday, often preparing it for the New Year. The flower fits well into the interior of the room, decorating and transforming it. One or more pots with a flowering plant are placed in a prominent place. The crop is also used for cutting. The inflorescences at the blooming bud stage retain freshness and appearance for 10 days, and at low temperatures – up to 18-20 days.
Forcing hippeastrum on video:
Hippeastrum is a beautiful flowering plant that will decorate any room. Recommendations regarding the care and maintenance of hippeastrum during flowering and dormancy will allow you to grow a strong and beautiful flower at home.